The number of offspring or seeds produced at each reproductive cycle by a plant is called clutch size For example, a plant produces 1000 seeds in its one season It is its clutch size Generally plants which large clutch size (produce large number of seeds) produce small seeds or fruits Their seeds and fruits have small amount of stored Gymnosperms Cycad Cones Maxfocus/iStock/Getty Images Plus The Coniferophyta division contains conifers, which have the greatest variety of species among gymnospermsMost conifers are evergreen (retain their leaves throughout the year) and include some of the largest, tallest and oldest trees on the planet Examples of conifers include pines,Particularly favorable does reproduction from seed con tribute significantly to maintenance and spread of the species (Andrejak and Barnes 1969, Maini 1974) Therefore, Baker's (1918b) suggestion that sexual reproduction is defective because of failure of seed set or low germinability of seeds was widely accepted for

Assignment Class 7 Reproduction In Plants
Seed reproduction examples
Seed reproduction examples-I really can't rememer, but I hope to see one in person someday seed, the characteristic reproductive body of both angiosperms (flowering plants) and gymnosperms (eg, conifers, cycads, and ginkgos)Essentially, a seed consists of a miniature undeveloped plant (the embryo), which, alone or in the company of stored food for its early development after germination, is surrounded by a protective coat (the testa)) Frequently small




13 Propagation Nc State Extension Publications
Sexual Reproduction Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction in which the two sexes, namely, male and female are involved Example 2 Case Based Soak a few seeds of Bengal gram (chana) and keep them overnight Drain the excess water and cover the seeds with a wet cloth and leave them for a day Make sure that the seeds do not become dry Sexual Reproduction in Plants – Unisexual and Bisexual The flowers are the reproductive parts of a plant The stamens are the male reproductive part and the pistil is the female reproductive part; Many plants propagate using pollen and seeds, but asexual reproduction is also common Explore how asexual plant reproduction occurs through the vegetative propagation of bulbs, tubers, rhizomes
40 Sexual Reproduction in Plants Mr C Biology 6 • The zygote grows into an embryo plant inside of a seed • The endosperm is the food store for the plant inside the seed (oils and fats) • Nonendosperm examples are broad bean, peanut and sunflowersVegetative reproduction results in new plant individuals without the production of seeds or spores Many different types of roots exhibit vegetative reproduction The corm is used by gladiolus and garlic Bulbs, such as a scaly bulb in lilies and a tunicate bulb in daffodils, are other common examples of this type of reproductionAnswer (1 of 4) As far as I know, all plants can reproduce asexually The degree to which this is possible without human interference will vary Plants' meristem tissue is basically undifferentiated, and if induced to grow roots, can become a new plant genetically identical to the original This
Answer (1 of 6) I really, truly, hope that you can think of two plants that produce seeds!Gymnosperms are any type of vascular plant that reproduce via an exposed seed While most flowering plants, known as angiosperms, have a seed enclosed in an ovary or fruit, gymnosperms (which means "naked seeds") do not have covers on their seeds Some examples of nonflowering plants that are classified as gymnosperms includeSeed plant introduction Origin and evolution of the seed habit The seed habit is the most complex and evolutionary successful method of sexual reproduction found in vascular plants Today, seed plants, gymnosperms ("Nacktsamer", ca 800 living species) and angiosperms ("Bedecktsamer", flowering plants, ca living species), are by far



Flowering Plant Reproduction




Pistil Definition Description Facts Britannica
Noun living or onceliving thing pistil Noun seedbearing female reproductive organ of a flower, consisting of an ovary, style (tube that delivers pollen to the ovary), and stigma (which receives pollen) sexual reproduction Noun type of reproduction in which a sperm fertilizes an egg to form a zygote sperm Apomixis is a form of asexual reproduction in some species of grasses The parent plant produces seeds without fertilization Fragmentation is another form of asexual reproduction It involves new plants growing from small parts of the parent plant that fall to the ground For example, animals or the wind can break stems or leaves off plants Gymnosperm seeds are different from angiosperm seeds because they lack a protective coating In angiosperms, this coating is called the ovary An example of an ovary is an apple where the seeds




Reproduction Different Modes Of Plant Reproduction Byju S
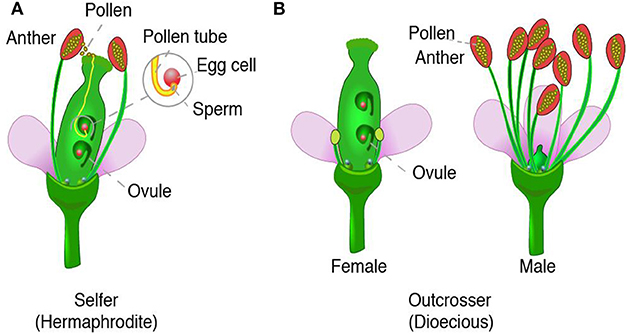



Flower Power A Close Look At Plant Reproduction Frontiers For Young Minds
Plant reproduction without seeds Not every plant grows from a seed Some plants, like ferns and mosses, grow from spores Other plants use asexual vegetative reproduction and grow new plants from rhizomes or tubers We can also use techniques like grafting or take cuttings to make new plantsAsexual reproduction in plants occurs in two fundamental forms vegetative reproduction and agamospermy Vegetative reproduction involves a vegetative piece of the original plant producing new individuals by budding, tillering, etc and is distinguished from apomixis, which is a replacement of sexual reproduction, and in some cases involves seedsSeed Dispersal by Water In this method of seed dispersal, seeds float away from their parent plant These are mainly seen in those plant which lives in water or nearby the water bodies like beaches, lakes, ponds etc Coconut, palm, mangroves, water lily, water mint, are a few examples of plants whose seed are dispersed by the water



1




Science Plant Reproduction Without Seed English Youtube
The process is a type of asexual reproduction The seeds develop and grow without the process of fertilization The seeds of some types Examples of asexual plant reproduction are commonplace Suckers Apples, bananas, cherries and raspberries all grow sprouts called "suckers" from spreading underground roots These grow into new plants;The reproductive part of a flowering plant is the flower Flowers are considered to be modified shoots Parts of a Flower Most flowers have both the male and female reproductive organs, but some bear either the male or the female sex organs
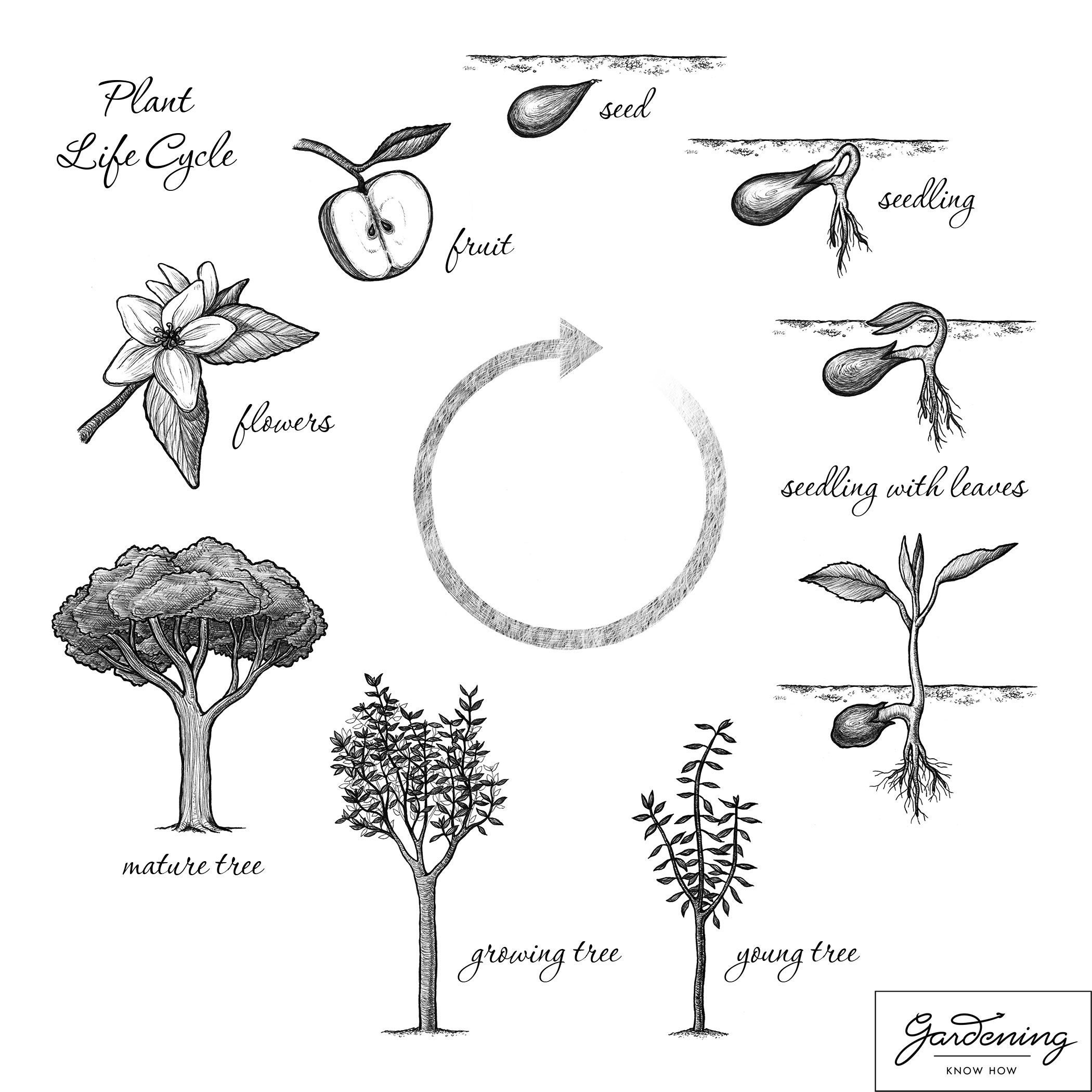



Basic Plant Life Cycle And The Life Cycle Of A Flowering Plant Gardening Know How




Biology Reproduction Notes
Seed – A plant's unit of reproduction, which includes the genetic material and any necessary nutrients to start the development of a new plant Symbiosis – A relationship between two organisms in which both benefit The cooperation between angiosperms and animals could be seen as an example of symbiosis Quiz 1In asexual reproduction in plants, plants are reproduced without the formation of seeds Following are a few ways in which plants reproduce asexually Vegetative Propagation As the name suggests, reproduction occurs through the vegetative parts of a plant such as stems, leaves, buds, and rootsPlant reproductive system, any of the systems, sexual or asexual, by which plants reproduce Asexual reproduction results in offspring that are identical to the parent plant Sexual reproduction involves new genetic combinations and results in offspring that are genetically different from the parent plants




Ncert Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction In Plants Arinjay Academy
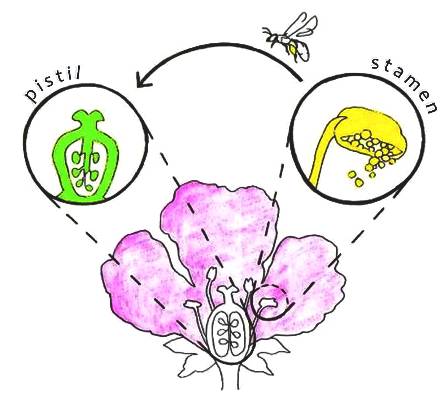



Flower Anatomy
Asexual reproduction in plants It is possible for plants to reproduce asexually (ie without fertilisation in flowers) Three methods of plant asexual reproduction areSeeds are an essential element of sexual reproduction in plants It is formed as the end product of sexual reproduction in plants and is exclusive only to angiosperms and gymnosperms Other dicot seeds examples include apples, plums and peaches Structure of a Monocotyledonous Seed Vegetative Propagation Have you ever thought if reproduction in the plant can take place without seeds?




Ppt On Seed Dispersal Powerpoint Slides




Sexual Reproduction In Plants Ck 12 Foundation
Reproduction plants can give rise to new plants without seeds, whereas in sexual Asexual reproduction In asexual reproduction new plants are obtained without production of seeds Vegetative propagation It is a type of asexual reproduction in which new plants are produced from roots, stems, leaves and buds Since reproduction is through theYes, it is possible In flowering plants, the roots, stem and leaves also help in reproduction This process is called Vegetative Propagation in Plants This method can be used to grow genetically and morphologically identical offspring from a parent plantSexual reproduction is a natural way of reproduction in humans, animals and the majority of plants also choose to reproduce sexually This type of reproduction is more complex and lengthy as compared to asexual reproduction Moreover, reproducing sexually gives the benefit of variation and offsprings are unique




Quotes About Plant Reproduction 23 Quotes




Solved Many Seed Plants Can Reproduce Sexually Or Asexually Chegg Com
If not, you might want to look into a radically new type food that is taking the world by storm I think it's called fwoop?Reproductive organs of plants in the first placeperform the function of reproduction The fruit protects the seeds from their premature distribution They are dry or juicy Seeds are formed inside the fruit, gradually ripening Some of them are equipped with devices that help spread, for example, a dandelion spreads to the wind Asexual reproduction involves the replication of chromosomes without the production of gametes or the need for sex Asexual reproduction pro duces offspring that are genetically identical to their parents Typical examples of this form of reproduction are the stolons ('runners') produced by strawberries (Fragaria species), and root sprouting
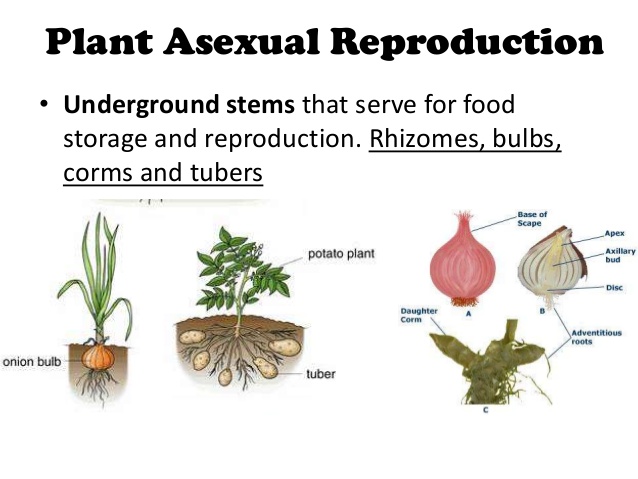



Advantages And Disadvantages Of Asexual Reproduction In Plants Science Online




13 Propagation Nc State Extension Publications
Reproduction in Angiosperms First, pollen falls on a flower's stigma In time, the sperm cell and egg cell join together in the flower's ovule The zygote develops into the embryo part of the seed Sexual Reproduction Germination Germination is the early stage of seed growthThere are thousands of examples of sexual reproduction in plants, so here are some examples of large groups of plants that reproduce sexually Ferns, such as horsetails or clubmolasses, which reproduce through spores Gymnosperms, such as the Maidenhair tree or the Scots pine, which reproduce through seeds Apomixis (asexual seed formation) is the result of a plant gaining the ability to bypass the most fundamental aspects of sexual reproduction meiosis and fertilization Without the need for male fertilization, the resulting seed germinates a plant that develops as a maternal clone




Gymnosperms Naked Seed Plants An Overview Of Biodiversity




Assignment Class 7 Reproduction In Plants
The flowers which contain either only the pistil or only the stamens are called unisexual flowersThe flowers which contain both stamens and pistil are called bisexual√100以上 seed reproduction examples Answer (1 of 15) This question asks how nonseed plants reproduce, nowhere in the question is it asking about plants that can produce by cloning, grafting, or sporulating which also produce by seeding The nonseed plants are bryophytes Mosses, Apomixis is a form of asexual reproduction in someSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants!
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/gymnosperm_reproduction-5ae33a4e0e23d90039a3dba5.jpg)



Gymnosperms Definition Examples And Reproduction




Biology Reproduction Notes
Example, while Canada thistle has been observed to produce as few as 680 seeds per plant, curly dock often produces more than 30,000 seeds per plant Vegetative reproduction The ability to reproduce vegetatively is a unique characteristic that promotes the survival of a perennial species In vegetative (asexual) reproduction, a new plant developsSexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete (such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another to produce a zygote that develops into an organism composed of cells with two sets of chromosomes () Sexual reproduction is the most common life cycle in multicellular eukaryotes, such as animals, fungiWhereas seed plants closed into pieces two inter alia, mango, guava, rambutan, beans, and others More about the material sample seed plants please learn here »Examples of seed plants Reproduction seed plants Seeds produced by seed plants produced from the process of pollination (pollen fall on white)
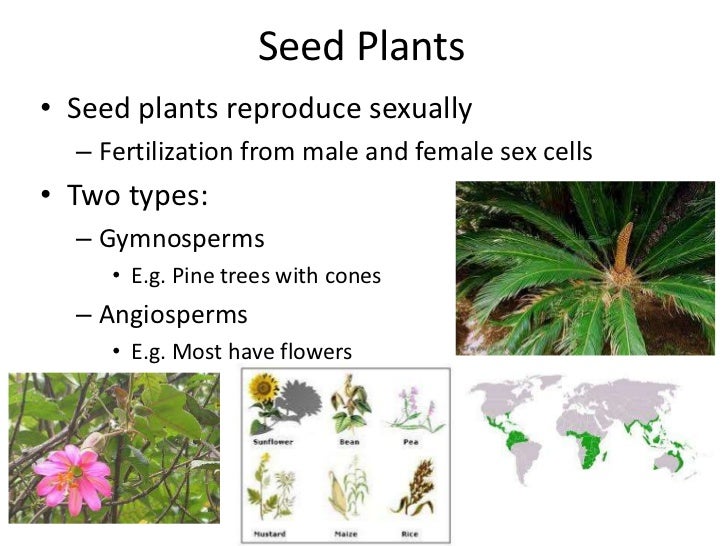



Plant Reproduction Seed Plants



Reproduction In Plants



Seed Png Teaching Resources
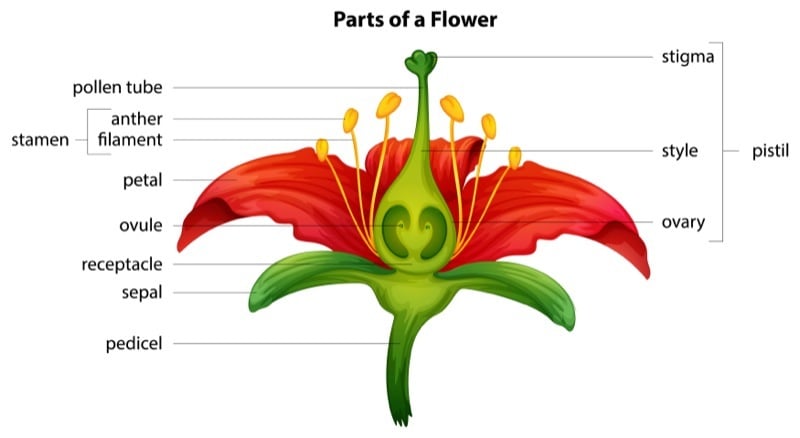



Plant Reproduction How Do Plants Reproduce
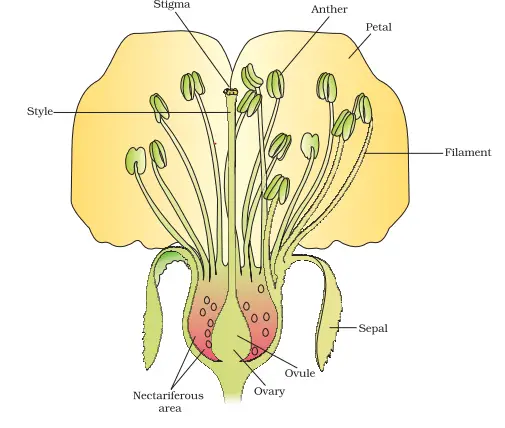



Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants Notes Chapter 2 Class 12 Biology




Plant Growth Reproduction And Life Cycle Lessons With Interactive Student Notebook Lessons Teaching Resources




Plant Reproduction Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Learnhive Cbse Grade 5 Science Reproduction In Plants Lessons Exercises And Practice Tests




There S More Than One Way To Make A New Plant Discovery Express




Lesson Explainer Types Of Reproduction Nagwa




Science Form 2 Science Is Awesome Biodiversity Classification Of Plants




Seed Wikipedia




Chapter 12 Plant Propagation
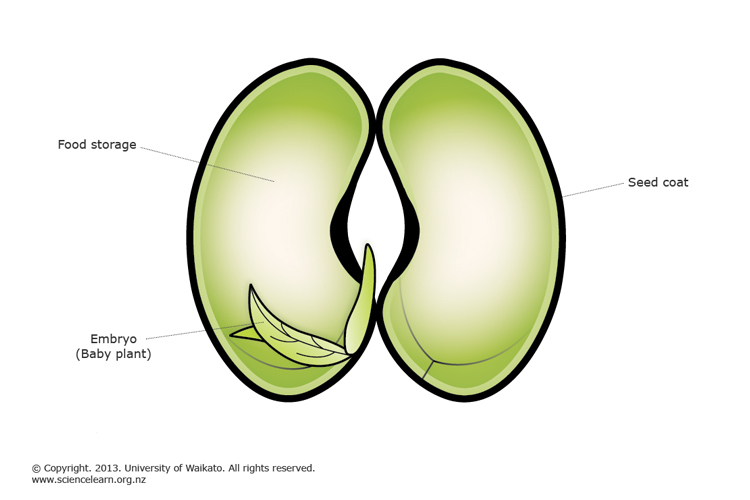



Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub
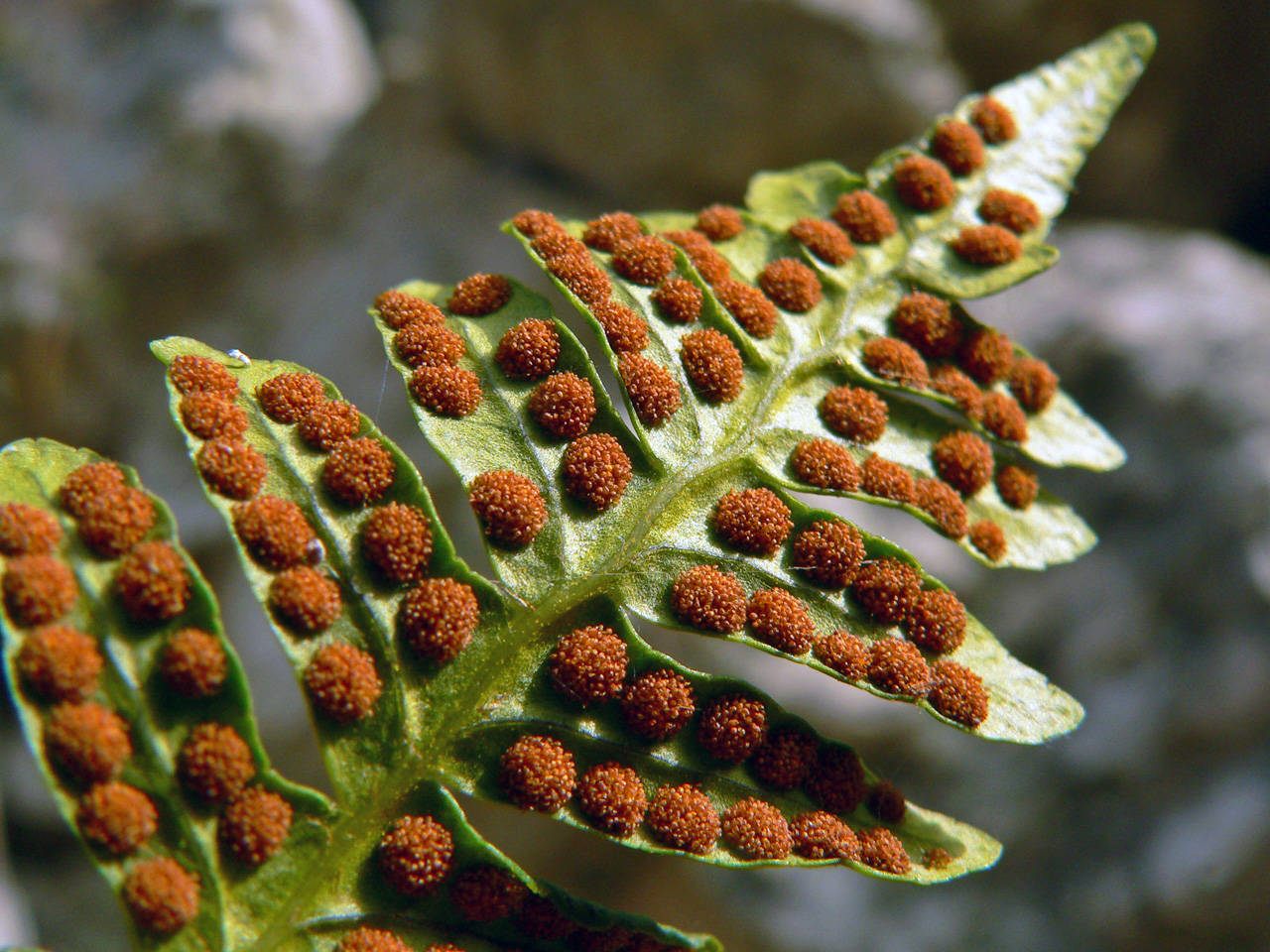




Fifth Grade Plant Reproduction Non Seed Plants



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants
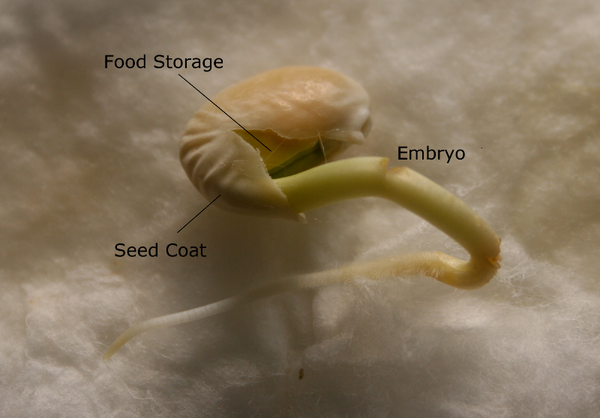




13 Propagation Nc State Extension Publications



Paramecium Parlor Comics Science With The Amoeba Sisters



An Introduction To The Structure And Reproduction Of Plants Plant Anatomy Plants Variation 375 Involve Differences In The Number Of Constituent Parts Such As Perianth Segments Leaflets In A Compound Leaf Etc




Pollination And Seed Dispersal Science Video For Kids Grades K 2




Plant Life Cycle Vector Illustration Labeled Educational Development Scheme With Seeds Cotyledon Seedling Flower And Adult Example Biology Basics With Reproduction Explanation Diagram Drawing Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration




Flowering Plants Life Cycle Examples Study Com




How Plants Are Classified Part 2 Reproduction Ppt Download
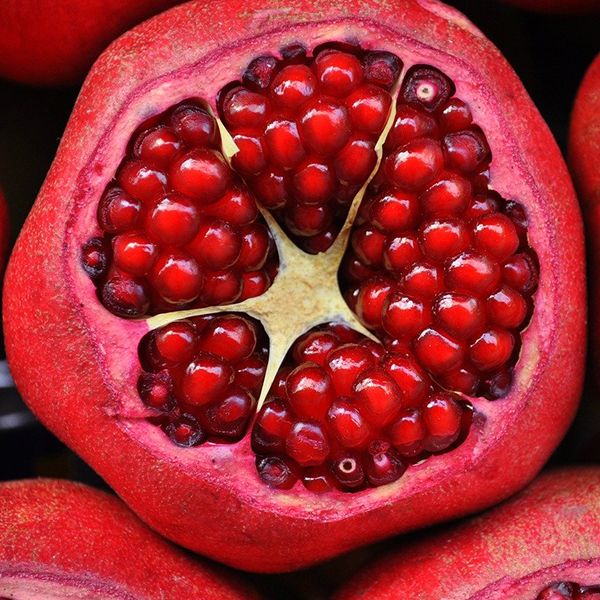




Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science




Examples Of Possible Log Log Relationships Between Direct And Accessory Download Scientific Diagram




Seeds Parts Germination Dispersal And Its Agents Videos And Examples
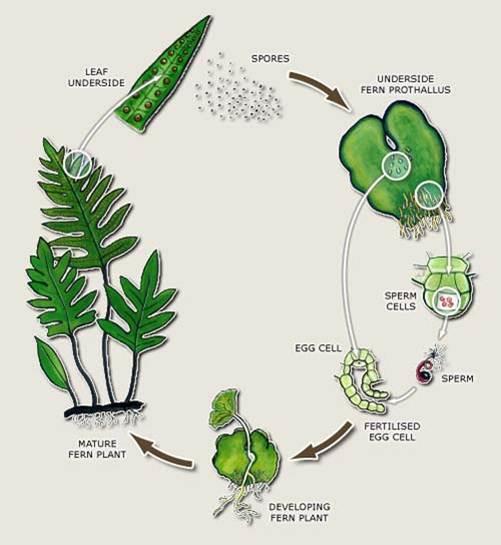



Seeds Vs Seedless Plants Biology Socratic



What Plants Reproduce Through Seeds Give Two Examples Quora
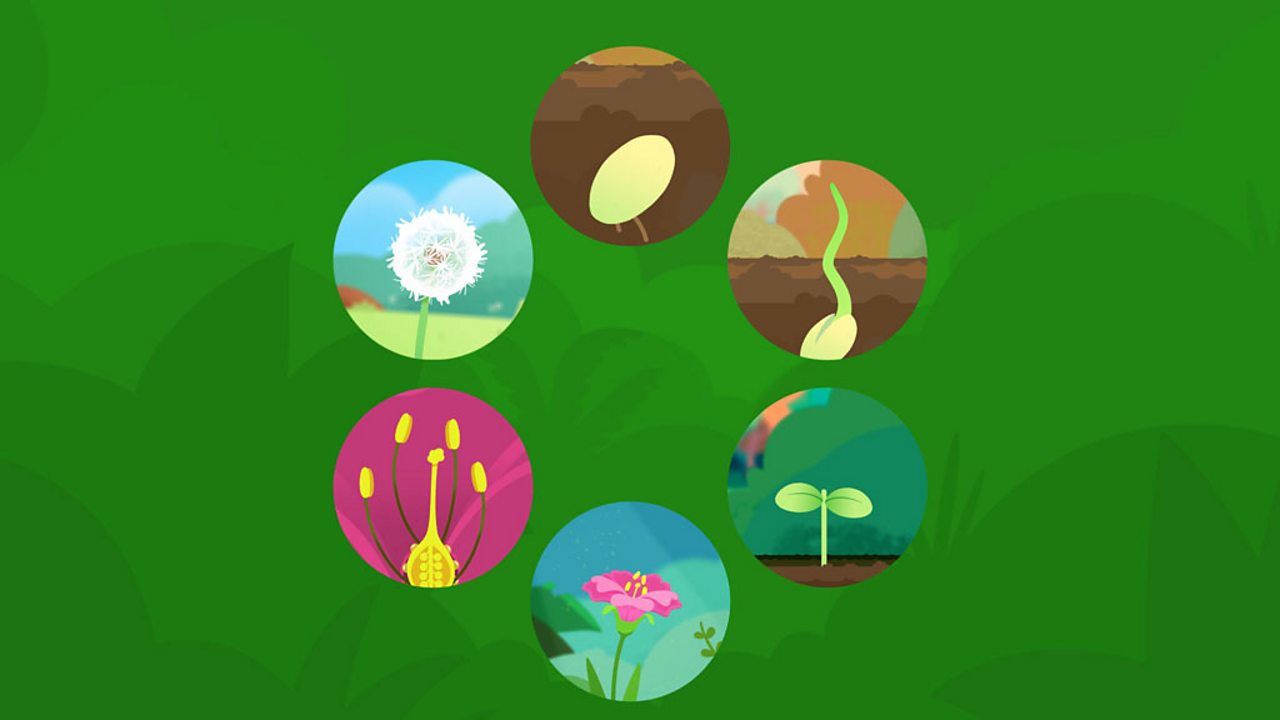




What Are The Stages Of A Plant S Life Cycle c Bitesize




The Seed Structure Functions Dispersion Concepts Videos Examples




Reproductive Plant Parts Osu Extension Service




Reproductive Systems And Evolution In Vascular Plants Pnas



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants



Sexual Reproduction In Plants Learn Biology Class 7 Amrita Vidyalayam Elearning Network




What Is A Seed Lesson For Kids Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Fruits Flowers And Seeds Biology Online Tutorial



Tomatosphere Tomatosphere The Life Cycle Of A Tomato Plant
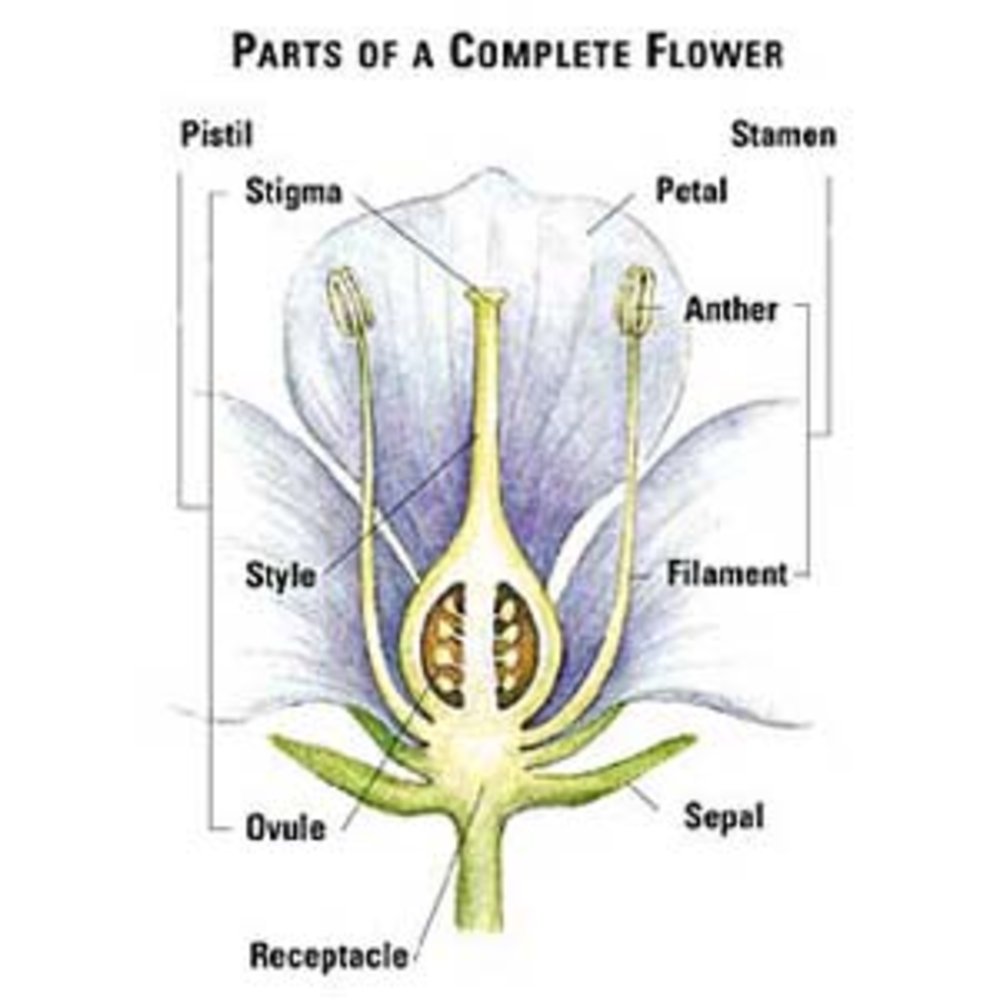



Flowers
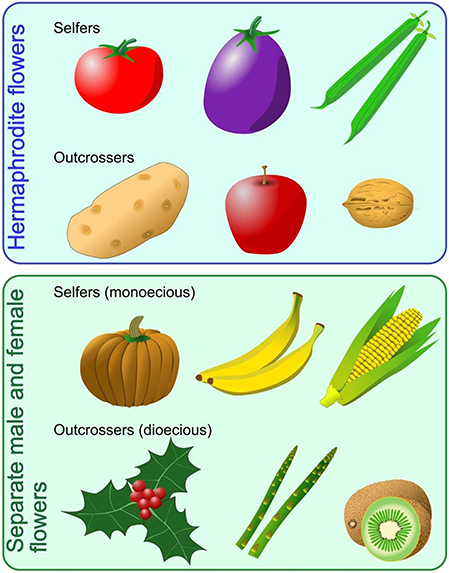



Flower Power A Close Look At Plant Reproduction Frontiers For Young Minds



Introduction To Reproduction Plants Animals Types Videos Examples




What Are The Seed Pods On My Pink Oleander Oleander Plants Seed Pods Wonderful Flowers




There S More Than One Way To Make A New Plant Discovery Express




4 02 Methods Of Plant Propagation Sexually And




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica
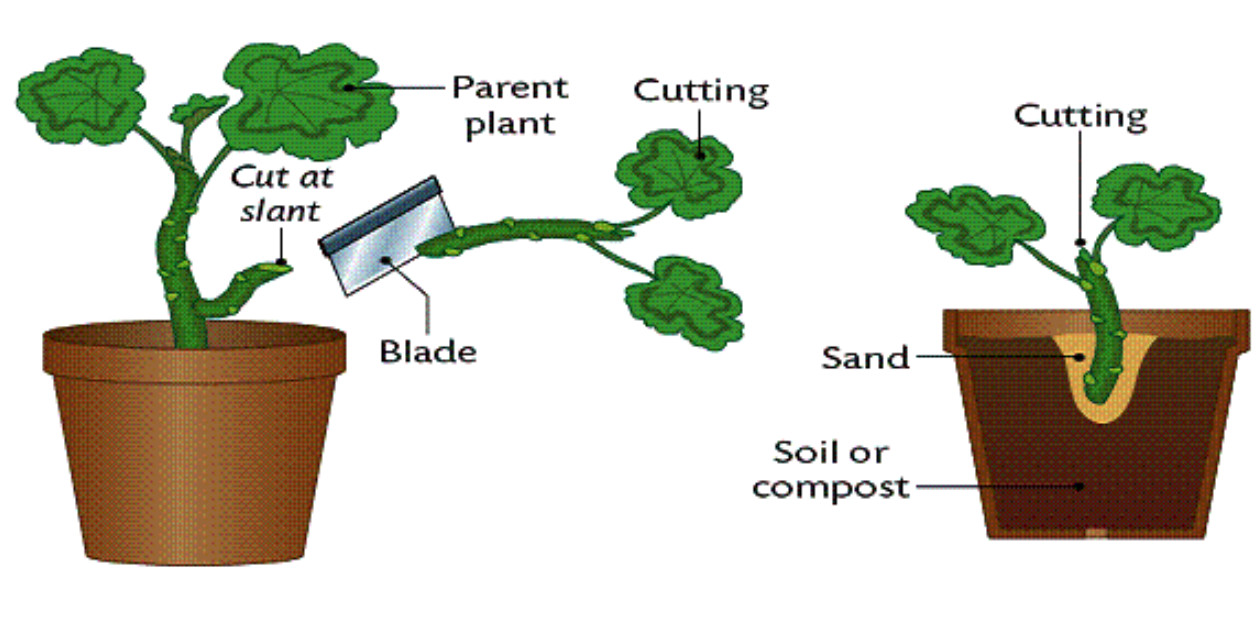



Asexual Reproduction In Plants Class 7 Reproduction In Plants Science




What Are The Different Ways Of Reproduction In Plants Give Examples Different How Or Rmjnaiion Take Place T Stud Evs Our Resources Meritnation Com



1



Plants A Text Book Of Botany Botany Plant Relations Very Common For Them To Branch So That The Flowers Appear In Clusters Sometimes Loose And Spray Like Sometimes Com Pact See Pigs
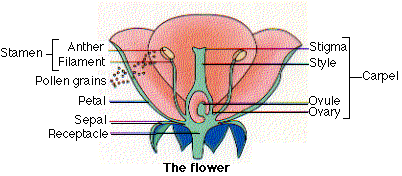



Sexual Reproduction In Angiosperms
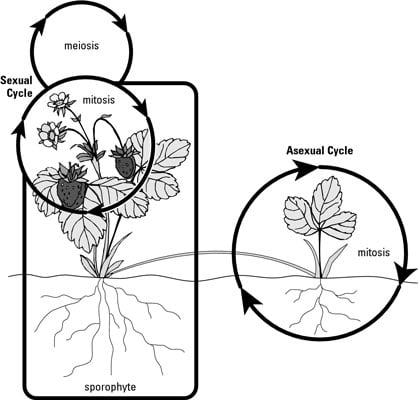



Plant Reproduction Dummies
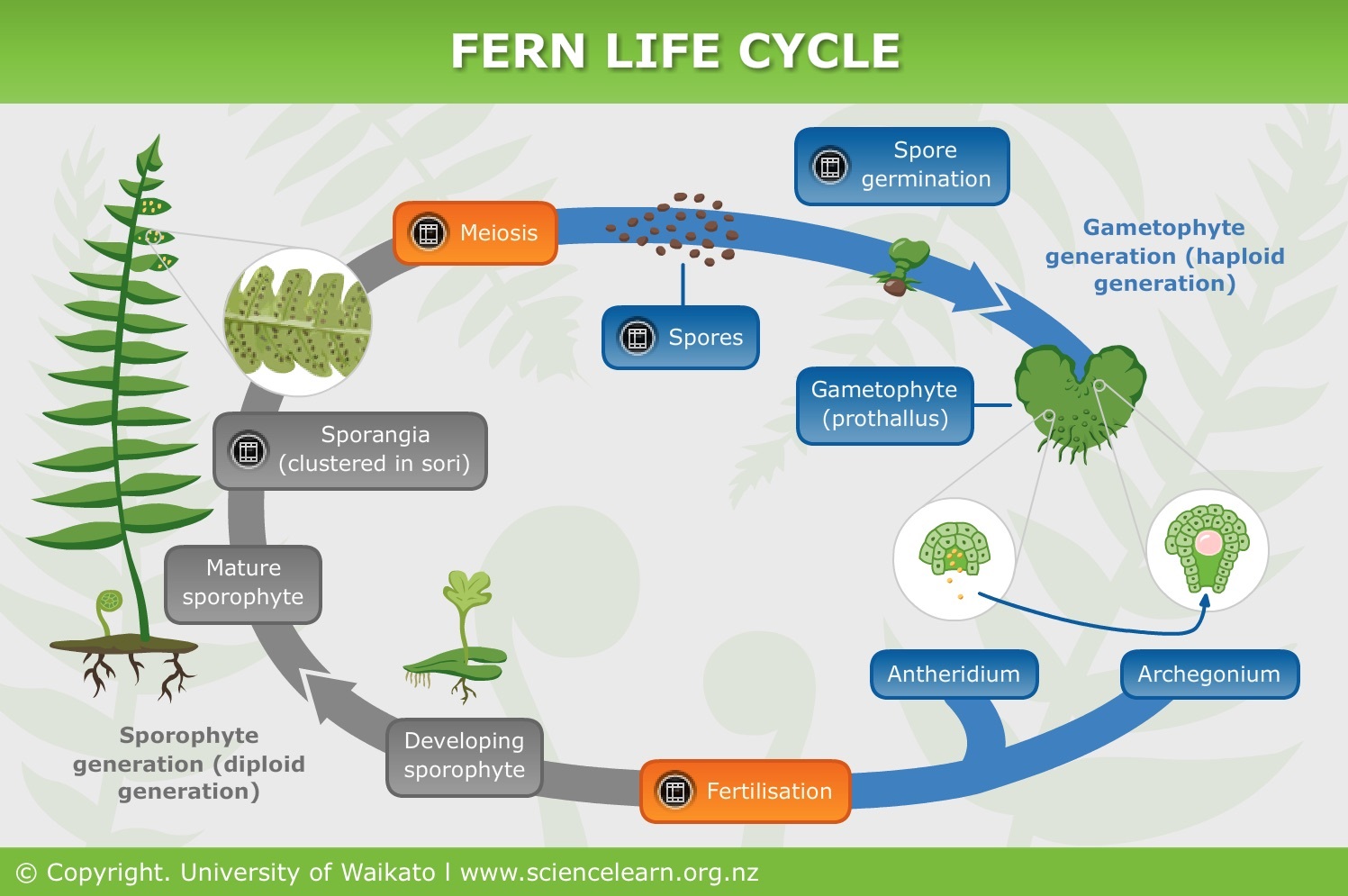



Plant Reproduction Without Seeds Science Learning Hub




Definition Of The Seed Advantages And Disadvantages Of Seed Propagation



3




Plant Propagation Sexual Reproduction Of Plants Ppt Download



Reproduction In Plants Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Examples Function Process Animal Different Organisms Chromosomes Organs




Life History Variation Among Species And Extreme Environment Biol 250 Docsity




Plant Reproduction Bioninja




What Are Some Forms Of Plant Propagation



Asexual Reproduction Biology Ii




Reproduction In Human And Plants Male Reproductive System




Seed Dormancy Intechopen




Flower Dissection Activity Review There Are Two Types Of Plants Plants With Seeds And Plants Without Seeds Ppt Download



Reproduction In Plants Psle Science




Plant Propagation Wikipedia




Life Cycle Of Different Plants




Asexual Reproduction In Plants Biology For Majors Ii




Pdf Examples Of Seed Dispersal By Entomochory




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica




Seed And Non Seed Plants Interactive Worksheet
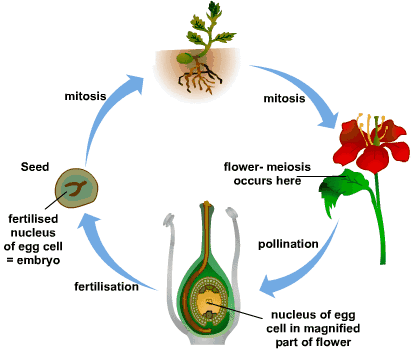



Mcq On Plant Reproduction By Biology Experts Notes Medium
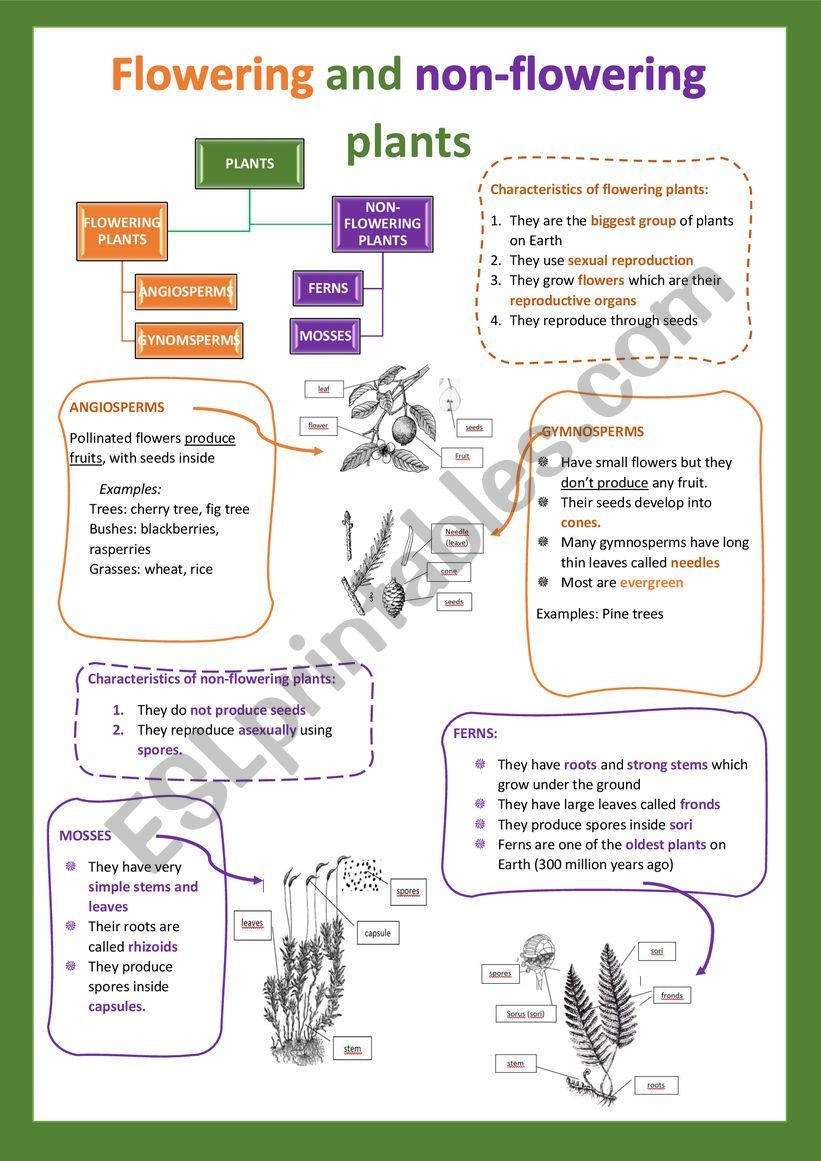



Flowering And Non Flowering Plants I Esl Worksheet By Cristinasuma
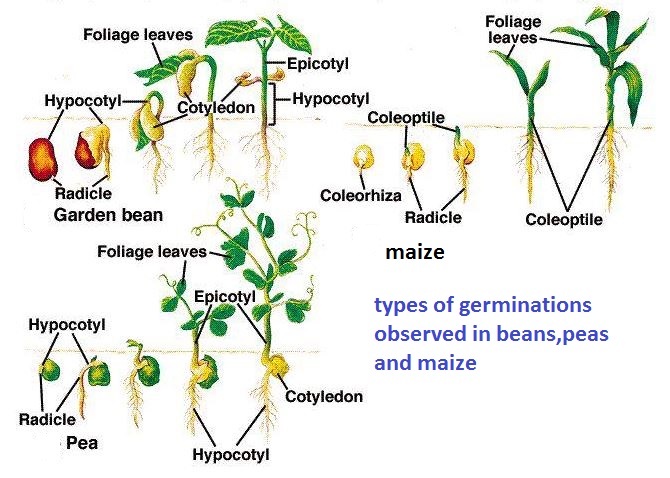



Elimu Plants
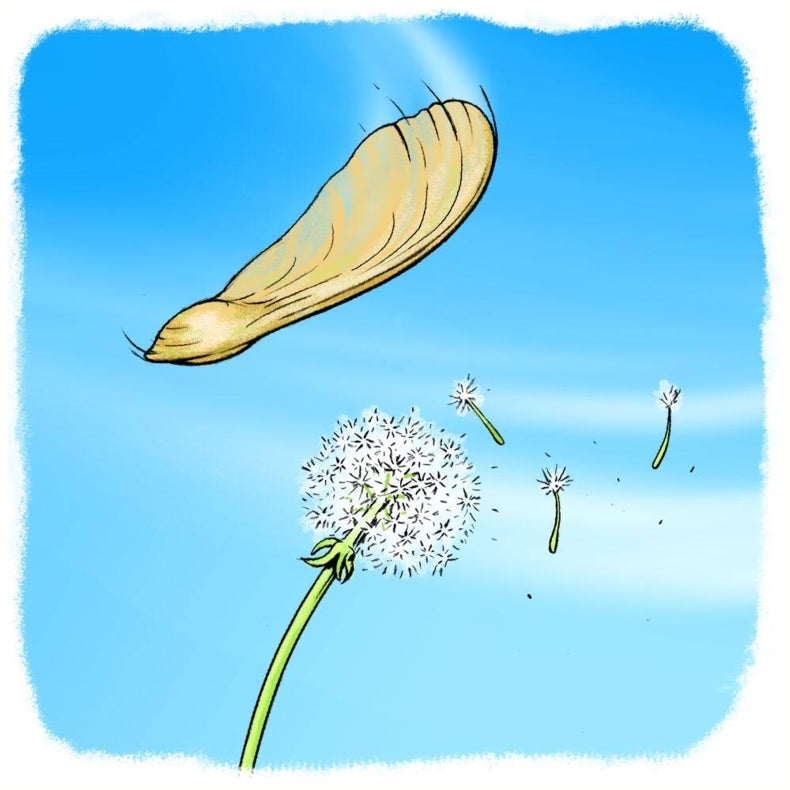




Gone With The Wind Plant Seed Dispersal Scientific American




Types Of Reproduction In Plants Youtube
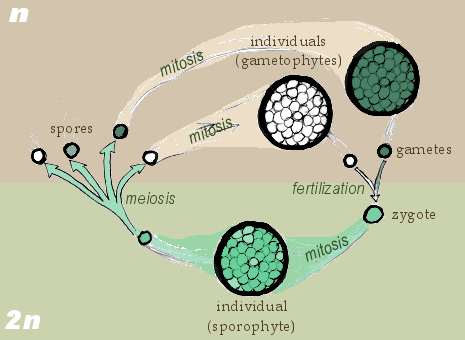



Plant Reproduction Organismal Biology



1




Seed Germination Types With Diagram




Seed Plant Evolution Ck 12 Foundation
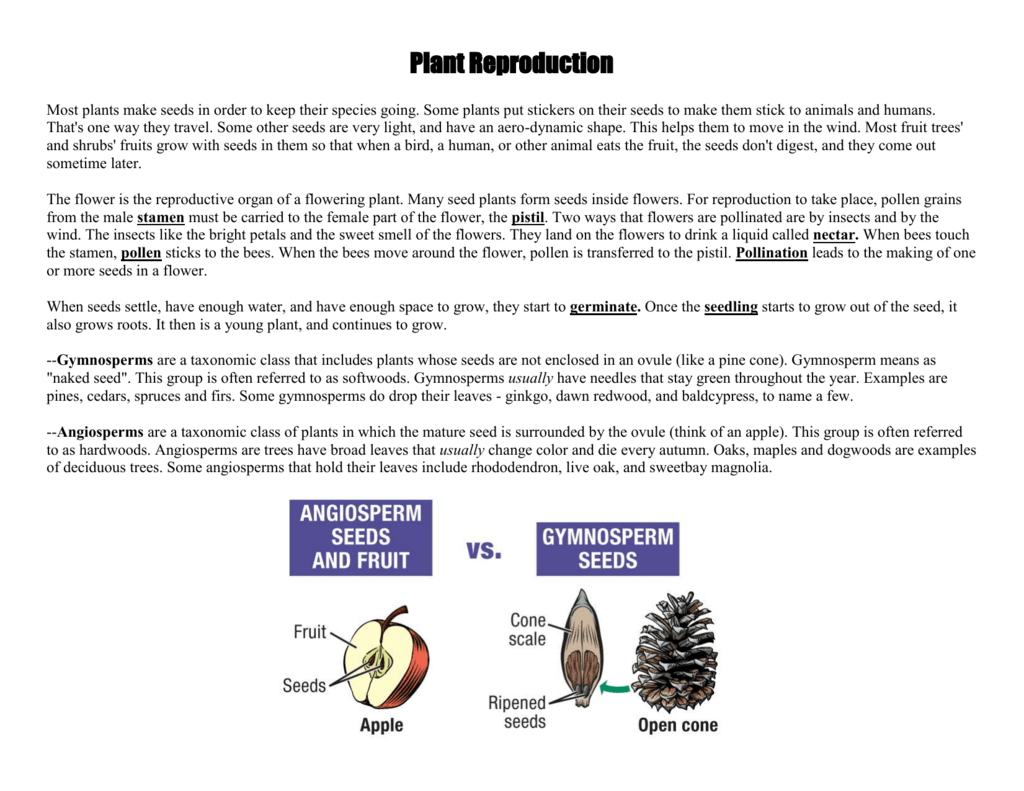



Plant Reproduction




Solved Flowering Plant Reproduction Development And Chegg Com




1 Nameany Three Agents Of Seed Dispersal Give Two Examples Of Each 2 Explain Germination Of Brainly In




What Are The Non Seed Plants With Examples Garden Bagan



Sexual And Asexual Reproduction In Plants
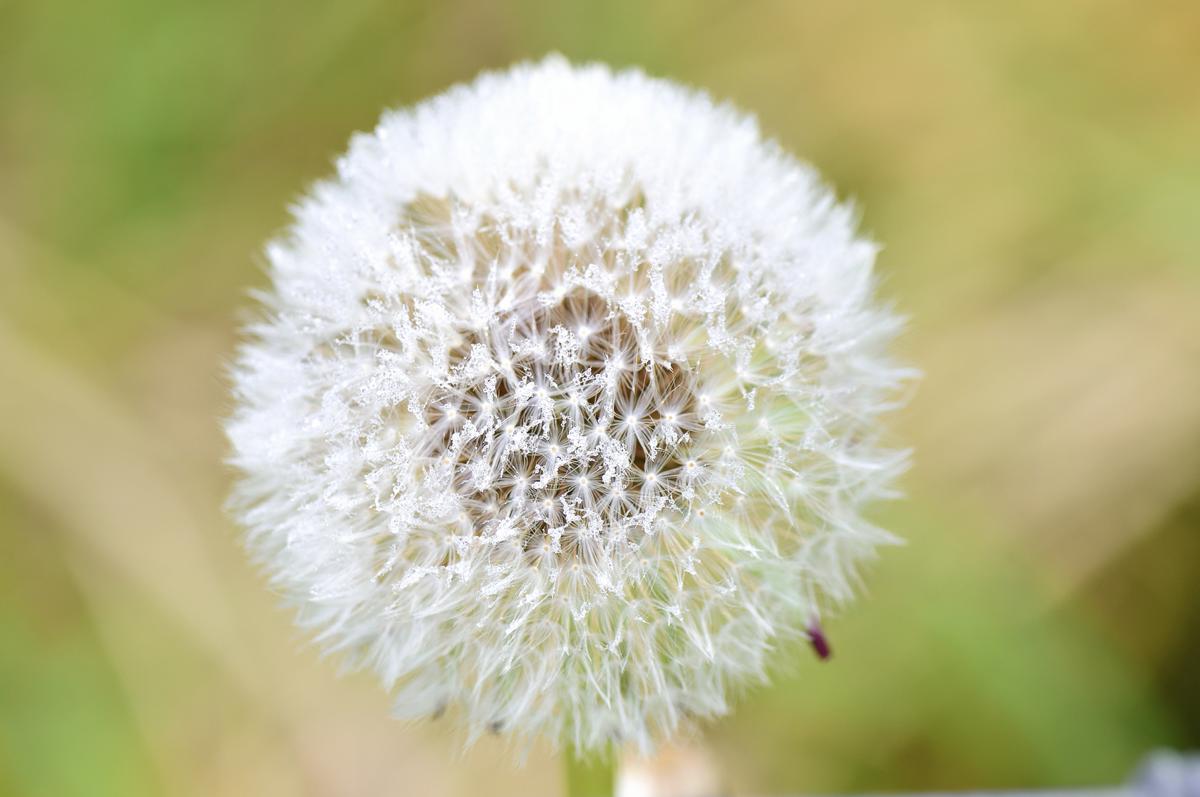




Asexual Reproduction In Plants Biology Wise



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿