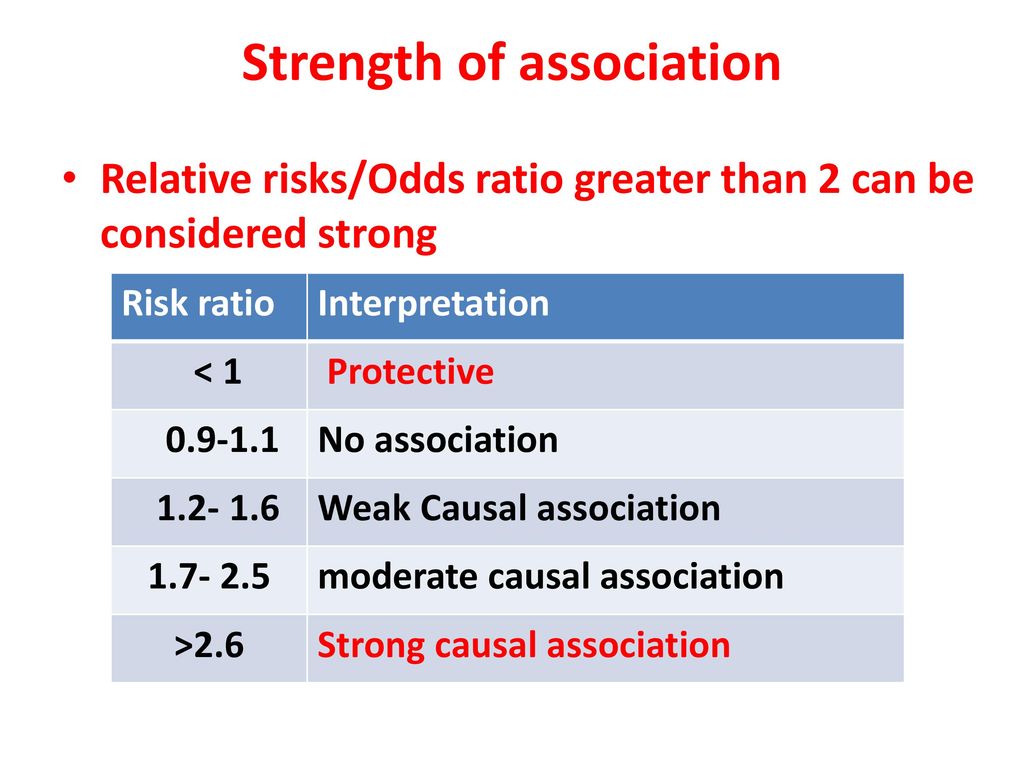
Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter to expected results, putting the onus on the researcher to justify them Similarly, you should find that increasing the incidence will increase the odds ratioJust as with RR, where the ratio of two risks was taken for two separate groups, a ratio of two odds can be taken for two separate groups to produce an odds ratio (OR) Instead of reporting how many times the risk one group bears relative to the other, it reports how many times the odds one group bears to the otherThe relative risk (or risk ratio) is an intuitive way to compare the risks for the two groups Simply divide the cumulative incidence in exposed group by the cumulative incidence in the unexposed group where CI e is the cumulative incidence in the 'exposed' group and CI u is the cumulative incidence in the 'unexposed' group
By Hatim Jaber Md Mph Jbcm Phd Ppt Download
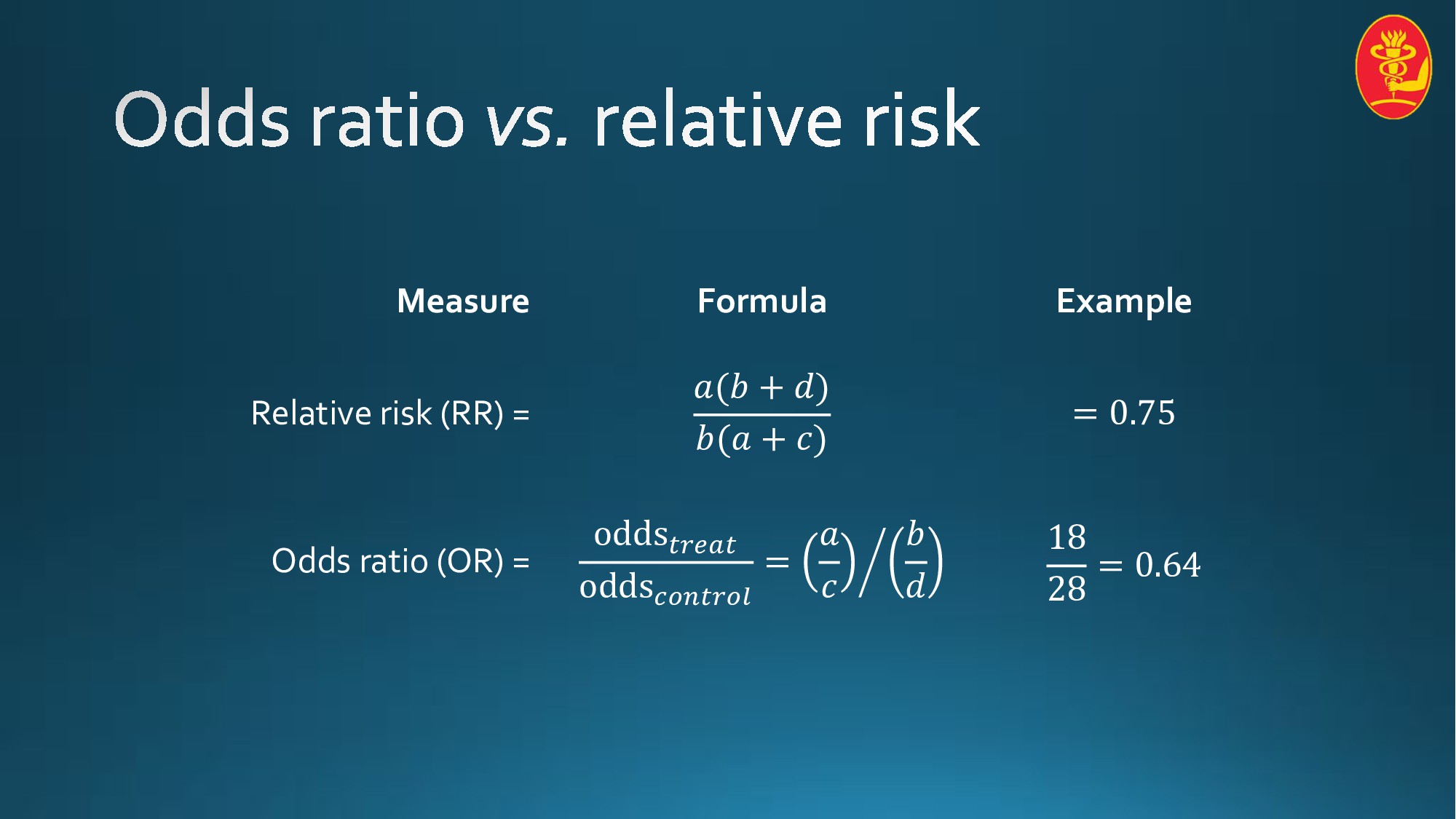
What is difference between odds ratio and relative risk
What is difference between odds ratio and relative risk-The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of cancer in smokers to the odds of cancer in nonsmokers OR = (a/b)/(c/d) = (ad)/(bc) The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokers RR = (a/(ab))/(c/(cd)) = (a(cd))/(c(ab))0 decreased risk Odds Ratio 0 5 10 15 More on the Odds Ratio Log Odds Ratio4 2 0 2 4




Relative Risk Reduction Can Be Relatively Misleading Youtube
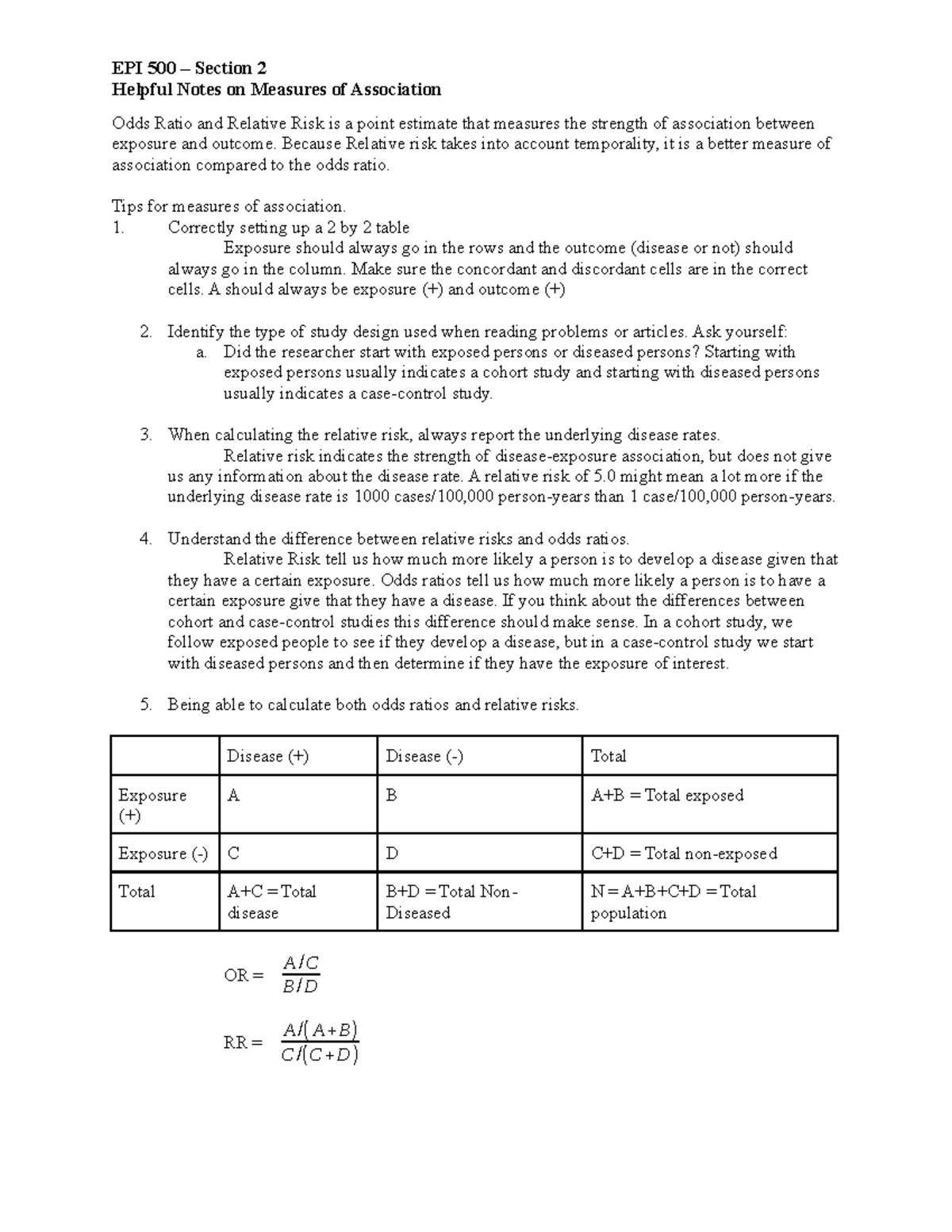
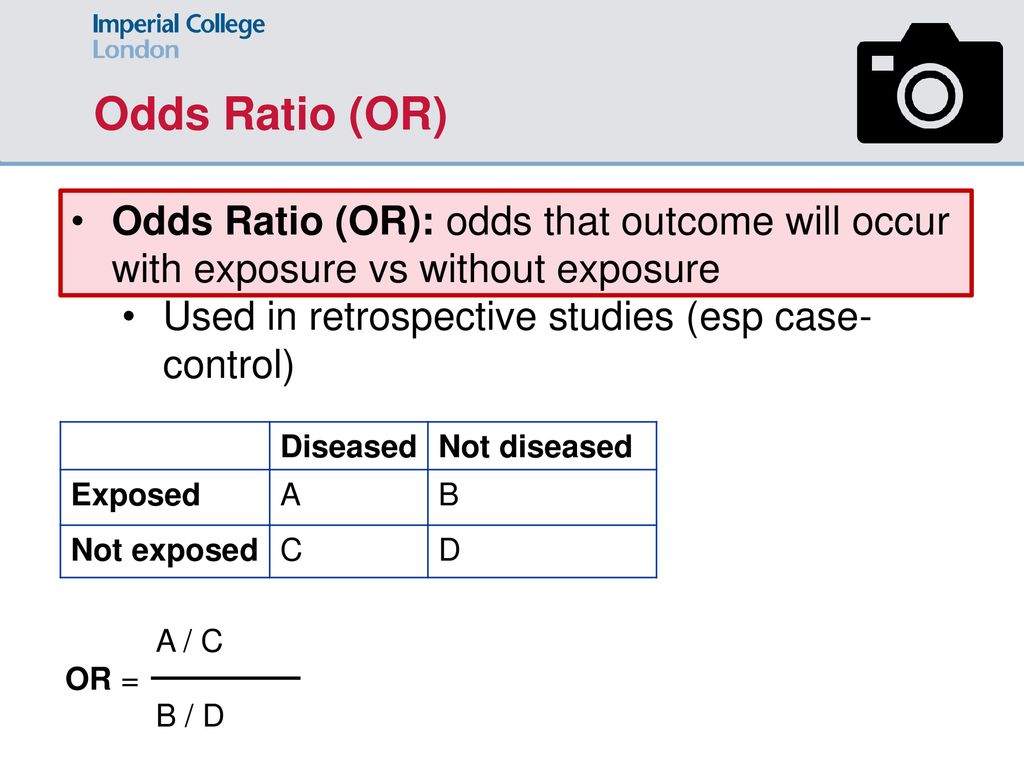
Relative Risk, Odds, and Fisher's exact test I) Relative Risk A) Simply, relative risk is the ratio of p 1/p 2 For instance, suppose we wanted to take another look at our Seat belt safety data from Florida Safety equipment Injury in use Fatal Nonfatal Total None 1,601 165,527 167,128 Seat belt 510 412,368 412,878Definition The Odds Ratio is a measure of association which compares the odds of disease of those exposed to the odds of disease those unexposed Formulae OR = (odds of disease in exposed) / (odds of disease in the nonexposed) Example I often think food poisoning is a good scenario to consider when interpretting ORs Imagine a group of friends went out toThen the odds ratio is computed by taking the ratio of odds, where the odds in each group is computed as follows OR = (a/b) / (c/d) As with a risk ratio, the convention is to place the odds in the unexposed group in the denominator
The relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a nonexposed groupA crude odds ratio can be converted to a crude risk ratio risk ratio = odds ratio/(1 − p0) (p0 ×The odds ratio supports clinical decisions by providing information on the odds of a particular outcome relative to the odds of another outcome In the endocarditis example, the risk (or odds) of dying if treated with the new drug is relative to the risk (odds) of dying if treated with the standard treatment antibiotic protocol
In medical literature, the relative risk of an outcome is often described as a risk ratio (the probability of an event occurring in an exposed group divided by the probability in a nonexposed group) Certain types of trial designs, however, report risk as an odds ratio This format is commonly expressed in cohort studies using logistic regressionOdds ratio), in which p0 is the outcome prevalence (risk) among the unexposed Some have applied this formula to an adjusted odds ratio to obtain an adjusted risk ratio 49 This method can produce biased risk ratios and incorrect confidenceIn prospective trials, it is simply a different way of expressing this association than relative risk




Effect Size Reporting Among Prominent Health Journals A Case Study Of Odds Ratios Bmj Evidence Based Medicine



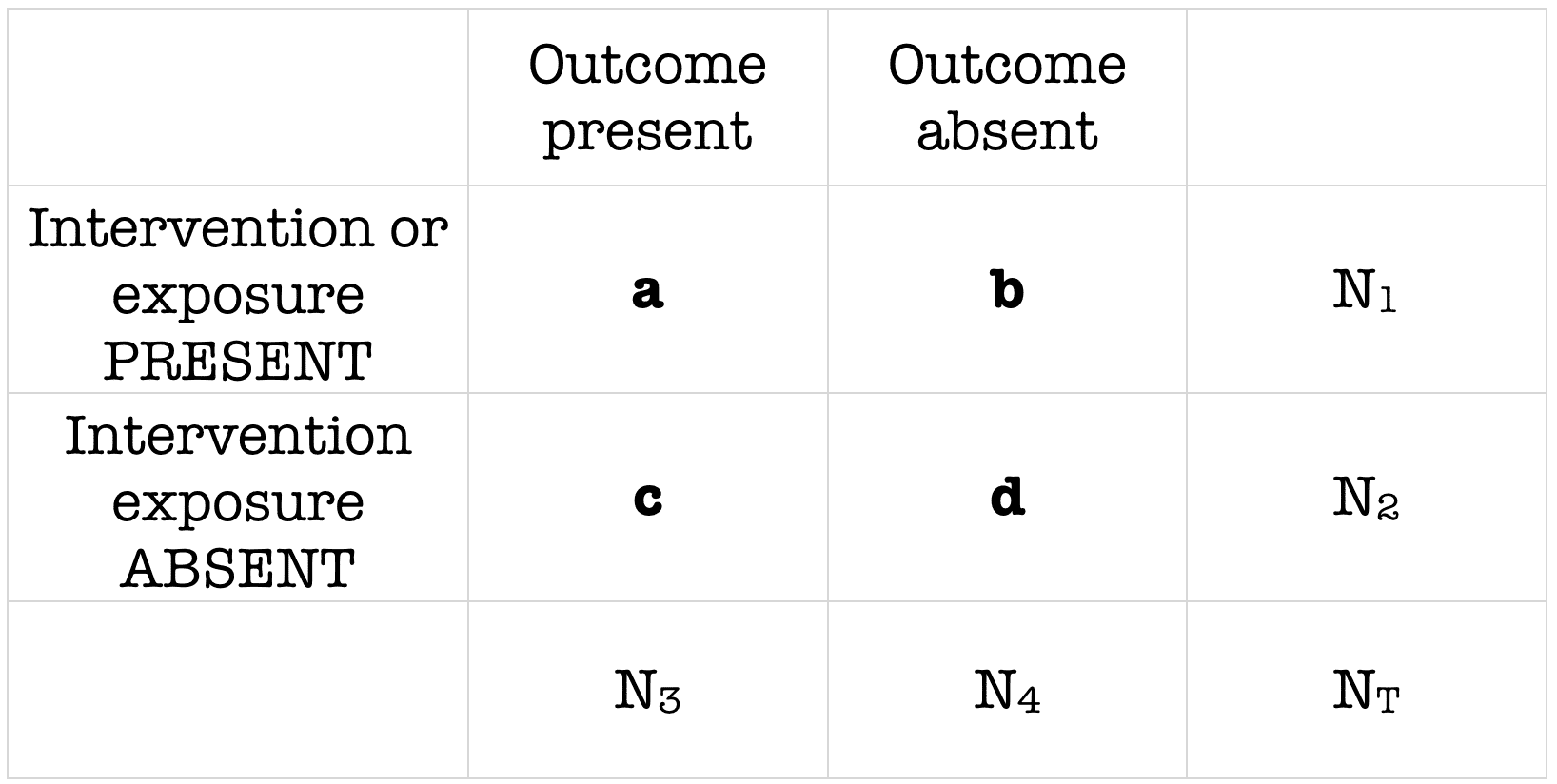
Silo Tips Download Transcript Measuring Risk In Epidemiology B D A C Measuring Risk In Epidemiology
Relative Risk and Odds Ratio Calculator This Relative Risk and Odds Ratio calculator allows you to determine the comparative risk of the occurrence of a significant event (or outcome) for two groups For example, suppose the members of one group each eat a kilo of cheese every day, and the members of another group eat no cheese, and you haveThe odds ratio can also be used to determine whether a particular exposure is a risk factor for a particular outcome, and to compare the magnitude of various risk factors for that outcome OR=1 Exposure does not affect odds of outcome OR>1 Exposure associated with higher odds of outcome OR<1 Exposure associated with lower odds of outcomeThe absolute risk is the probability of an event in a sample or population of interest The relative risk (RR) is the risk of the event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group



Measures Of Risk In Epidemiology Made Easy Youtube




By Hatim Jaber Md Mph Jbcm Phd Ppt Download
The odds ratio (OR) is a ratio of 2 numbers, like the relative risk we have 3 options OR = 1 The odds in the first group are the same as those in the second So no evidence that drinking wine can either OR >Once we calculate the odds ratio and relative risk, we may also be interested in computing confidence intervals for these two metrics A 95% confidence interval for the odds ratio can be calculated using the following formula 95% CI for odds ratio = exp (ln (OR) – 196*SE (ln (OR))) to exp (ln (OR) – 196*SE (ln (OR)))Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculated




March 28 Analyses Of Binary Outcomes 2 X 2 Tables Ppt Download




Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology
The risk of failure with SF was 96/351 (27%) vs 32/350 (9%) with HP The RR was 3 This has a very intuitive meaning risk of failure with SF was three times more likely than HP Odds Ratio The OR is a way to present the strength of association between riskRELATIVE RISK AND ODDS RATIO Risk and Odds just seemed the same to me for a long time Since then, I have come to understand to important difference Lets start with Relative Risk Relative Risk can be addressed by asking the following question How many times more likely is an exposed group to develop aOdds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a r



Www Jstor Org Stable



Exercise On Calculation Of Relative Risk Rr Chegg Com
For estimates of relative risk ratios, this becomes logarithmOR = odds ratioA confidence interval for the MantelHaenszel odds ratio in StatsDirect is calculated using the Robins, Breslow and Greenland variance formula (Robins et al, 1986) or by the method of Sato (1990) if the estimate of the odds ratio can not be determined A chisquare test statistic is given with its associated probability that the pooled odds




Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology




Relative Risks Odds Ratios Relative Measures Two Binomials Coursera
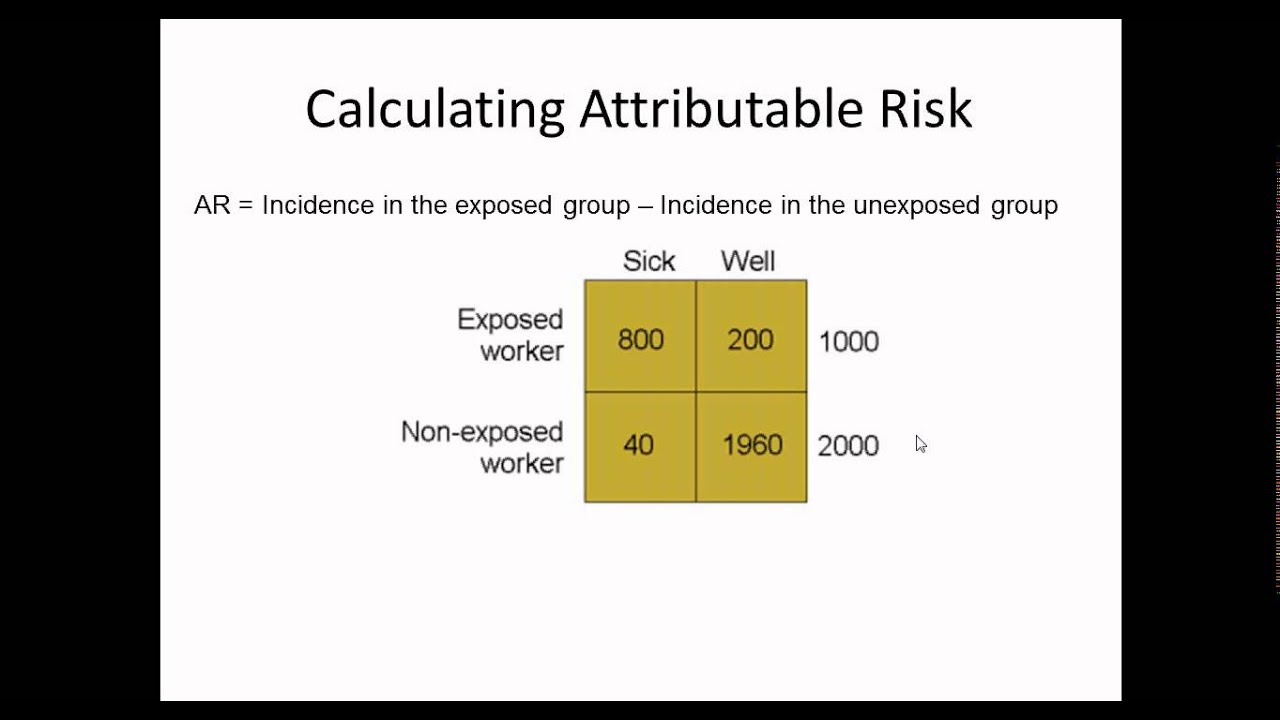
In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studies In prospective studies, Attributable risk or risk difference is used to quantify risk in the exposed group that is attributable to the exposure In retrospective studies, attributable risk can not be calculated directly but population attributable risk1 The odds of having the disease in the exposed group are higher than the unexposedAs an extreme example of the difference between risk ratio and odds ratio, if action A carries a risk of a negative outcome of 999% while action B has a risk of 990% the relative risk is approximately 1 while the odds ratio between A and B is 10




Odds Risks And Other Numbers Needed To Complicate Things Choi 16 Anaesthesia Wiley Online Library




Ppt Exploratory Data Analysis With Two Qualitative Variables Powerpoint Presentation Id
0 increased risk log OR = 0 no difference in risk log OR <The odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative risk otherwise In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea is reduced by 75% for the intervention relative to theIt is assumed that, if the prevalence of the disease is low, then the odds ratio approaches the relative risk Case control studies are relatively inexpensive and less timeconsuming than cohort studies In this case the odds ratio (OR) is equal to 16 and the relative risk (RR) is equal to 865




Society For Birth Defects Research And Prevention



Measures Of Association Studocu
Relative Risk (RR) is a ratio of probabilities or put another way it is one probability divided by another Odds Ratio (OR) is a ratio or proportion of odds I just remember that odds ratio is a ratio of odds and probability isn't a ratio of odds (AKA it is the other option) Relative Risk = Probability /Percent increase = (Risk Ratio lower bound – 1) x 100 Percent decrease = (1 – Risk Ratio upper bound) x 100 It's worth stating again when comparing two proportions close to 1 or 0, the risk ratio is usually a better summary than the raw difference Odds Ratios We now turn to odds ratios as yet another way to summarize a 2 x 2 tableSon of risks between groups, the ratio of risks, or the relative risk, is a statistic of choice Formally, if ˇ 1 is the probability of the event in group 1, and ˇ 2 is the probability of the event in group 2, then the relative risk is RR= ˇ 1 ˇ 2 The reason of preferring relative risk over the difference of risks RD= ˇ 1 ˇ 2



Cran R Project Org Web Packages Targeted Vignettes Riskregression Html




Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj
The relative risk (RR) and the odds ratio (OR) are the two most widely used measures of association in epidemiology The direct computation of relative risks isThe basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring programOdds = Probability / (1probability) Odds ratio (OR) = ratio of odds of event occurring in exposed vs unexposed group Odds ratio are used to estimate how strongly a variable is associated with the outcome of interest;



Data Analysis For The Bsc Year Ppt Download




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood
Relative measures of effect are risk ratio (ie the ratio between two incidence proportions), incidence rate ratio (the ratio between two incidence rates), and OR (the ratio between two odds) The risk difference is an absolute measure of effect (ie the risk of the outcome in exposed individuals minus the risk of the same outcome in unexposed)Although used as a measure of effect size from logistic regressions and casecontrol studies, they are poorly understood This paper provides practical advice for authors and readers on converting odds ratios to relative risks The odds ratio is a common measure in medical research of the effect size comparing two groups (treatments or riskRisk difference This study addresses the measures of effect, that is, the measures that are used to compare the frequency of disease (or other outcome) between two groups The measures of effect are generally expressed as relative risks and odds ratios (OR) (relative measures of effect) or as risk difference



Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy On Vimeo




How Can We Convert Rate Ratio To Odds Ratio
The relative risk is different from the odds ratio, although the odds ratio asymptotically approaches the relative risk for small probabilities of outcomesIf IE is substantially smaller than IN, then IE/(IE IN) IE/IN Similarly, if CE is much smaller than CN, then CE/(CN CE) CE/CN Thus, under the rare disease assumption = () () = In practice the odds ratio is commonly used forThe risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control group A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk or odds ratio >Odds ratios are a necessary evil in medical research;



1



Academic Oup Com Ije Article Pdf 24 2 464 24 2 464 Pdf
Relative Risk vs Odds ratio Relative Risk vs Odds ratio Watch later Share Copy link Info Shopping Tap to unmute If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your deviceAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy &Risk ratios At a minimum, the only change that needs to be done to get risk ratios is to change the link function that relates the mean value of the response variable to the linear predictor For estimates of odds ratios, this is logit (ie the logarithm of the odds of the mean);




Ppt Moving Beyond Odds Ratios Estimating And Presenting Absolute Risk Differences And Risk Ratios Powerpoint Presentation Id




Pdf Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat
OR = (p1/ (1p1)) * ((1p0)/p0) OR * (p0/ (1p0)) = p1/ (1p1) (1p0)/ (OR*p0) = (1p1)/p1 (1p0)/ (OR*p0) = 1/p1 1 1 (1p0)/ (OR*p0) = 1/p1 (OR*p0 (1p0))/ (OR*p0) = 1/p1 (OR*p0)/ (OR*p0 (1p0)) = p1 p1 = (OR*p0)/ (OR*p0 (1p0)) Since RR = p1/p01 indicates a heightened probability of the outcome in the treatment group The two metrics track each other, but are not equalSafety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators




Odds Ratios And Relative Risks Of T2d Diagnosis By Bmi Categories Download Scientific Diagram




Atrial Fibrillation As Risk Factor For Cardiovascular Disease And Death In Women Compared With Men Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Of Cohort Studies The Bmj
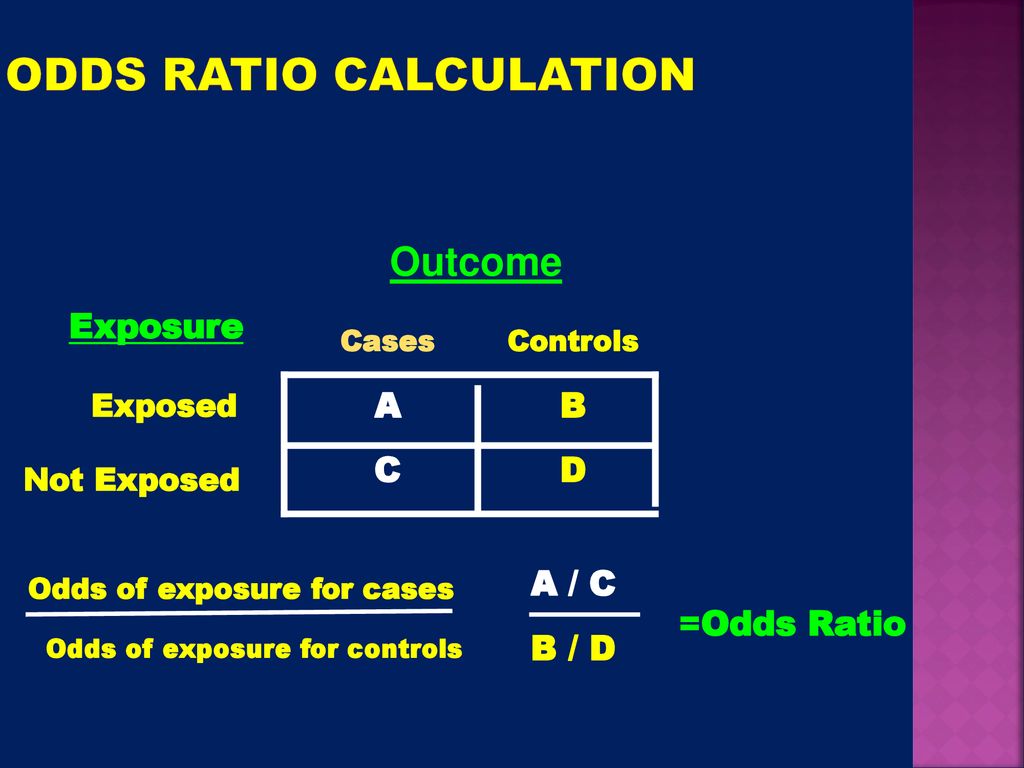
Sometimes, we see the log odds ratio instead of the odds ratio The log OR comparing women to men is log(144) = 036 The log OR comparing men to women is log(069) = 036 log OR >Odds Ratio = (a/c) / (b/d) = ad /bc An Odds Ratio of unity means that cases are no more likely to be exposed to the risk factor than controls Odds ratio in a matched study In a 11 matching, a case is paired with a control based on a similar characteristic (eg age), and the exposure isRelative risk, Risk difference and Odds ratio When the data to be analyzed consist of counts in a crossclassification of two groups (or conditions) and two outcomes, the data can be represented in a fourfold table as follows Several statistics can be calculated such as relative risk and risk difference, relevant in prospective studies, and




Calculation And Interpretation Of Odds Ratio Or And Risk Ratio Rr Youtube




Odds Ratios The Odd One Out Stats By Slough
For example, an odds of 001 is often written as 1100, odds of 033 as 13, and odds of 3 as 31 Odds can be converted to risks, and risks to odds, using the formulae;When the rare disease assumption does not hold, the odds ratio can overestimate the relative risk If the absolute risk in the control group is available, conversion between the two is calculated by where RR = relative risk;The interpretation of an odds is more complicated than for a risk The simplest way to ensure that the interpretation is correct is to first convert the odds into a risk




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal



1




Epidemiology Mph 531 Analytic Epidemiology Case Control Studies Ppt Download




Relative Risks Odds Ratios The Relative Risk Two Binomials Coursera




Pdf The Relative Risks Of Using Odds Ratios



Www Jstor Org Stable



Risk And Numbers Needed To Treat Litfl Ccc




Relative Risk Reduction Can Be Relatively Misleading Youtube



2




Ma 12 13 Lecture Notes 7 Relative Risks And Odds Ratios Studocu



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia



Http Www Cmaj Ca Highwire Filestream Field Highwire Adjunct Files 0 Eappendix Dev Pdf




How To Calculate An Odds Ratio Youtube
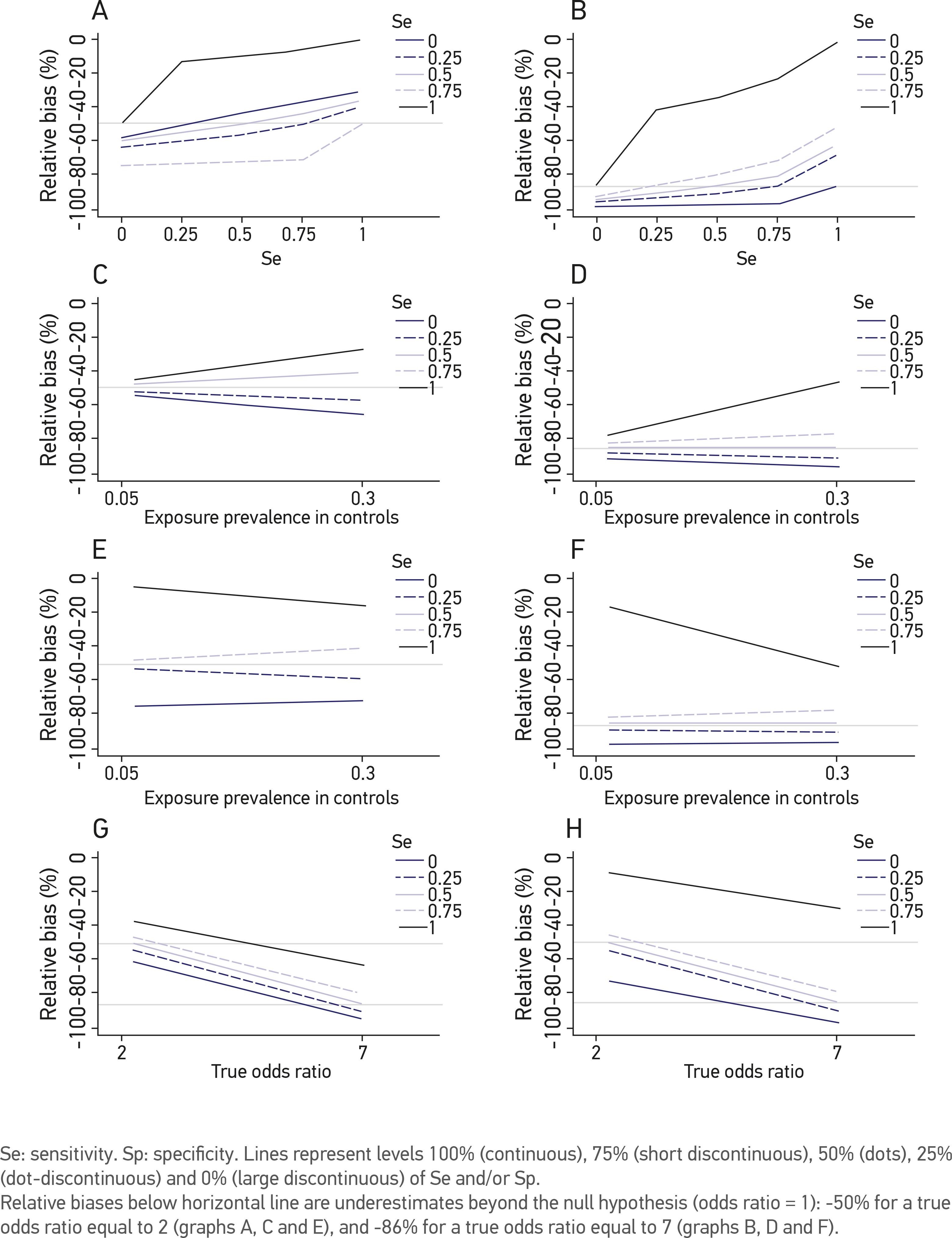



Scielo Brasil The Effect Of Misclassification Error On Risk Estimation In Case Control Studies The Effect Of Misclassification Error On Risk Estimation In Case Control Studies




How To Calculate Relative Risk 3 Steps With Pictures Wikihow



How To Read A Forest Plot Cochrane Uk




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube




Statistics 0 Lecture 7 Tuesday September 13 Ppt Download




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Ger1000 Chapter 4 More On Observational Studies Studocu



Http Www Biostat Jhsph Edu Fdominic Teaching Bio656 Software Meta Analysis Pdf




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology




Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio And 95 Confidence Intervals For Download Scientific Diagram




Ppt Evaluating Results Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Epidemiology Mph 531 Analytic Epidemiology Case Control Studies Ppt Download




Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk



Www Jstor Org Stable




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




The Following Results Were Obtained In An Chegg Com




Relative And Absolute Risk Video Explanation Osmosis




Pdf Using Sas Procedures Freq Genmod Logistic And Phreg To Estimate Adjusted Relative Risks A Case Study Semantic Scholar
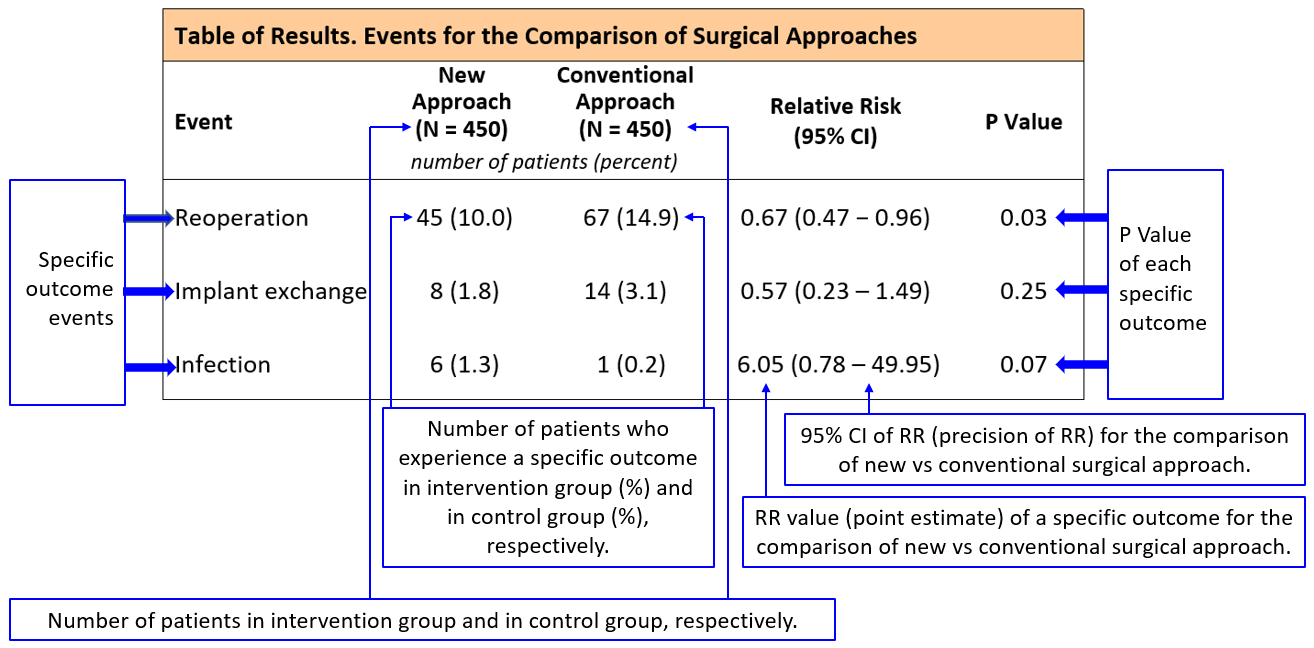



Interpreting Results From Randomized Trials




Epidemiology Knowledge Amboss



1




Risks Of And Risk Factors For Covid 19 Disease In People With Diabetes A Cohort Study Of The Total Population Of Scotland The Lancet Diabetes Endocrinology




Pdf Odds Ratio Relative Risk Absolute Risk Reduction And The Number Needed To Treat Which Of These Should We Use



Med Mahidol Ac Th Ceb Sites Default Files Public Pdf Academic 16 Race612 Handout Measurement in epidemiology16 Pdf




A Most Odd Ratio American Journal Of Preventive Medicine



Forest Plots Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios Of Detecting Fecal Download Scientific Diagram



Www Iapsmupuk Org Journal Index Php Ijch Article Download 1402 1044



Atrium Lib Uoguelph Ca Xmlui Bitstream Handle 1873 B Relative Risk And Odds Ratios Examples Pdf Sequence 8




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Number Needed To Harm Wikipedia




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj
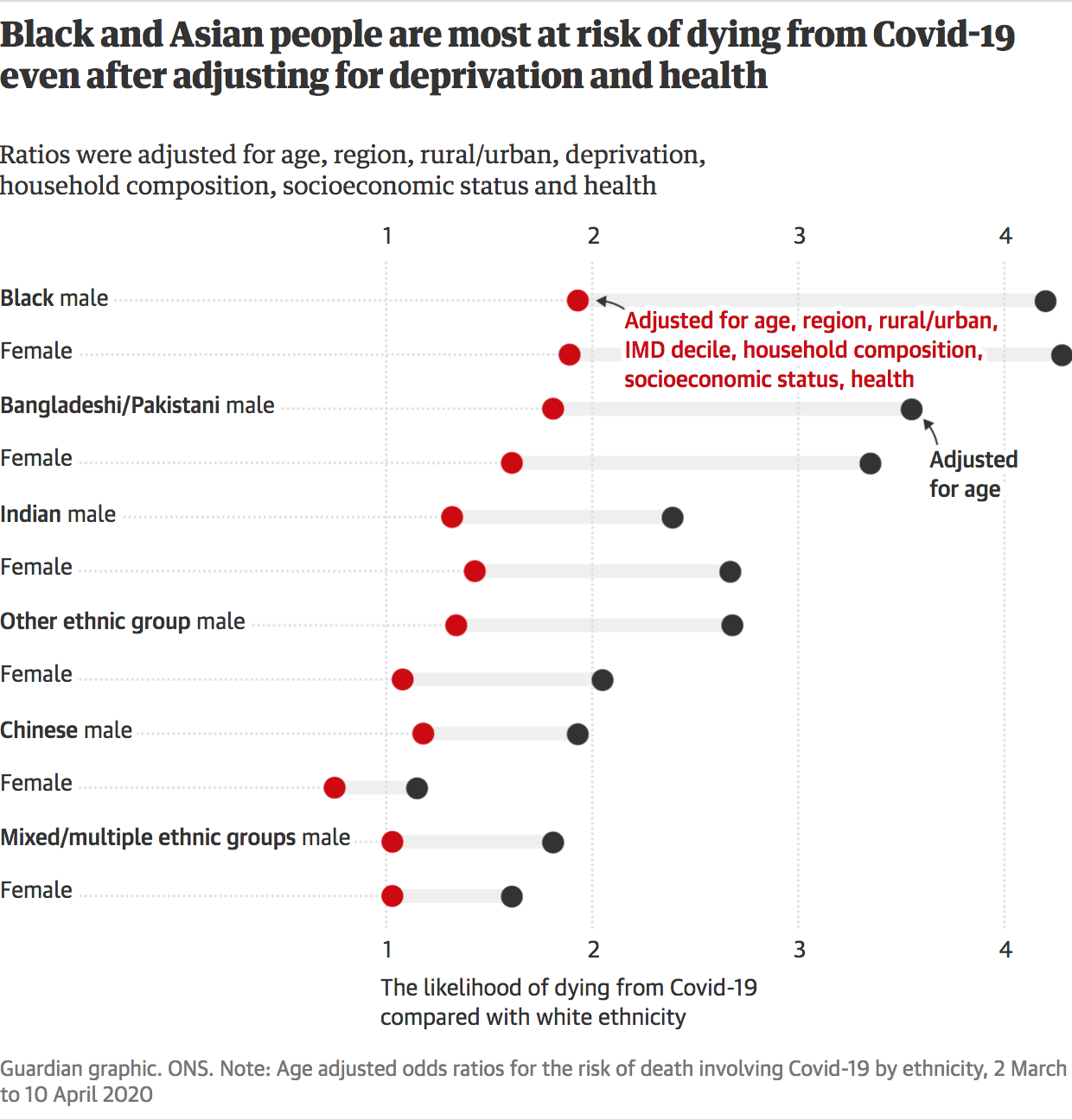



Against All Odds How To Visualise Odds Ratios To Non Expert Audiences Henry Lau



Http Www Floppybunny Org Robin Web Virtualclassroom Stats Basics Articles Odds Risks Proportions Odds Risks Sistrom 04l Pdf




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology



Q Tbn And9gcs7g3 Oy3gxo7fbk7uvklwexnnbqcmd7m5bqd Ghq64ww9hd4dh Usqp Cau




Ppt Chapter 11 Estimating Risk Is There An Association Powerpoint Presentation Id




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence
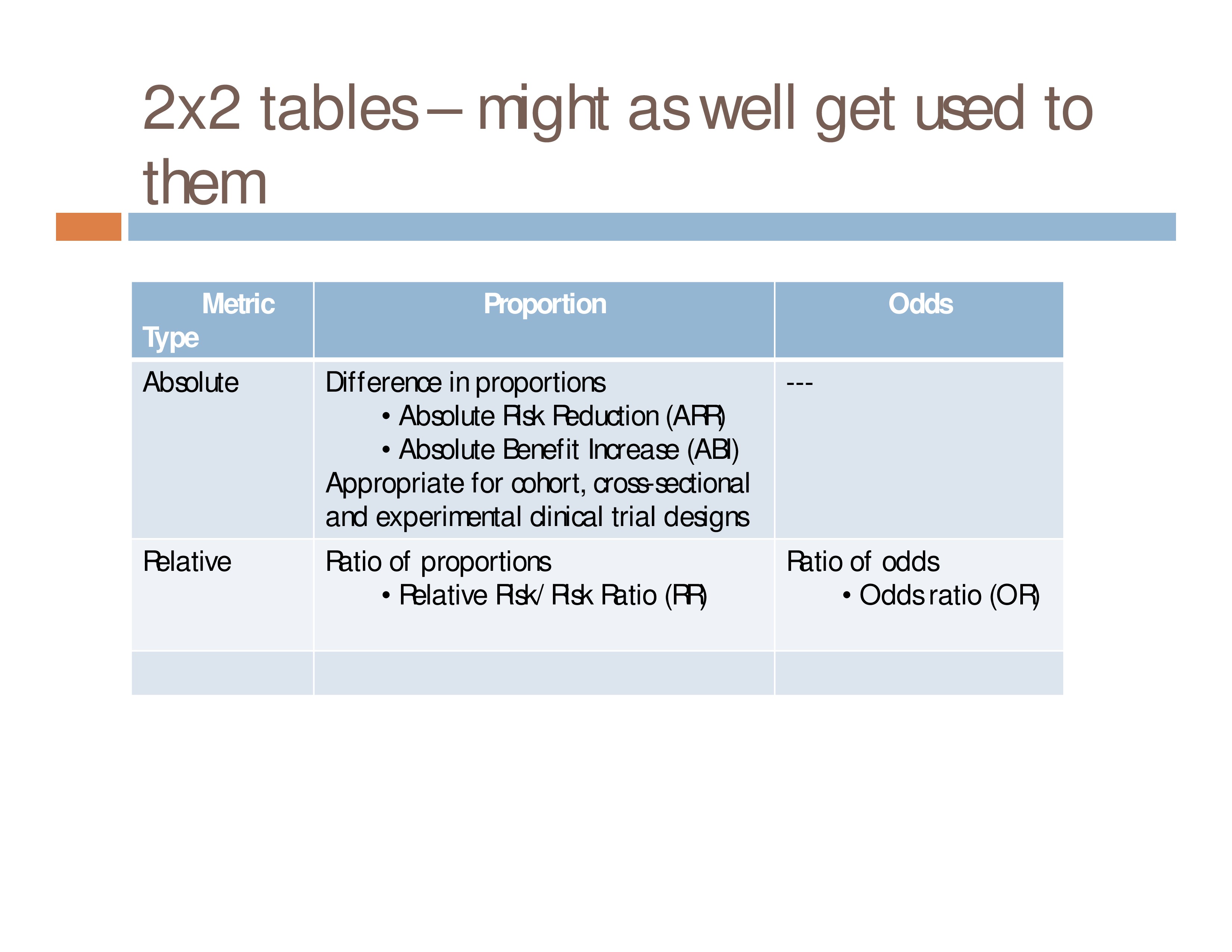



Event Based Measures Of Effect Size Asha Journals Academy



Www Academicpedsjnl Net Article S1876 2859 16 3 Pdf



Www2 Sjsu Edu Faculty Gerstman Statprimer Case Control Pdf




Propensity Score Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Chart Patch Likelihood Proportion Within Length




Pdf The Use Of Odds Ratio In Large Population Studies Warning To Readers




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Assessing Heterogeneity Of Treatment Effect Estimating Patient Specific Efficacy And Studying Variation In Odds Ratios Risk Ratios And Risk Differences Statistical Thinking
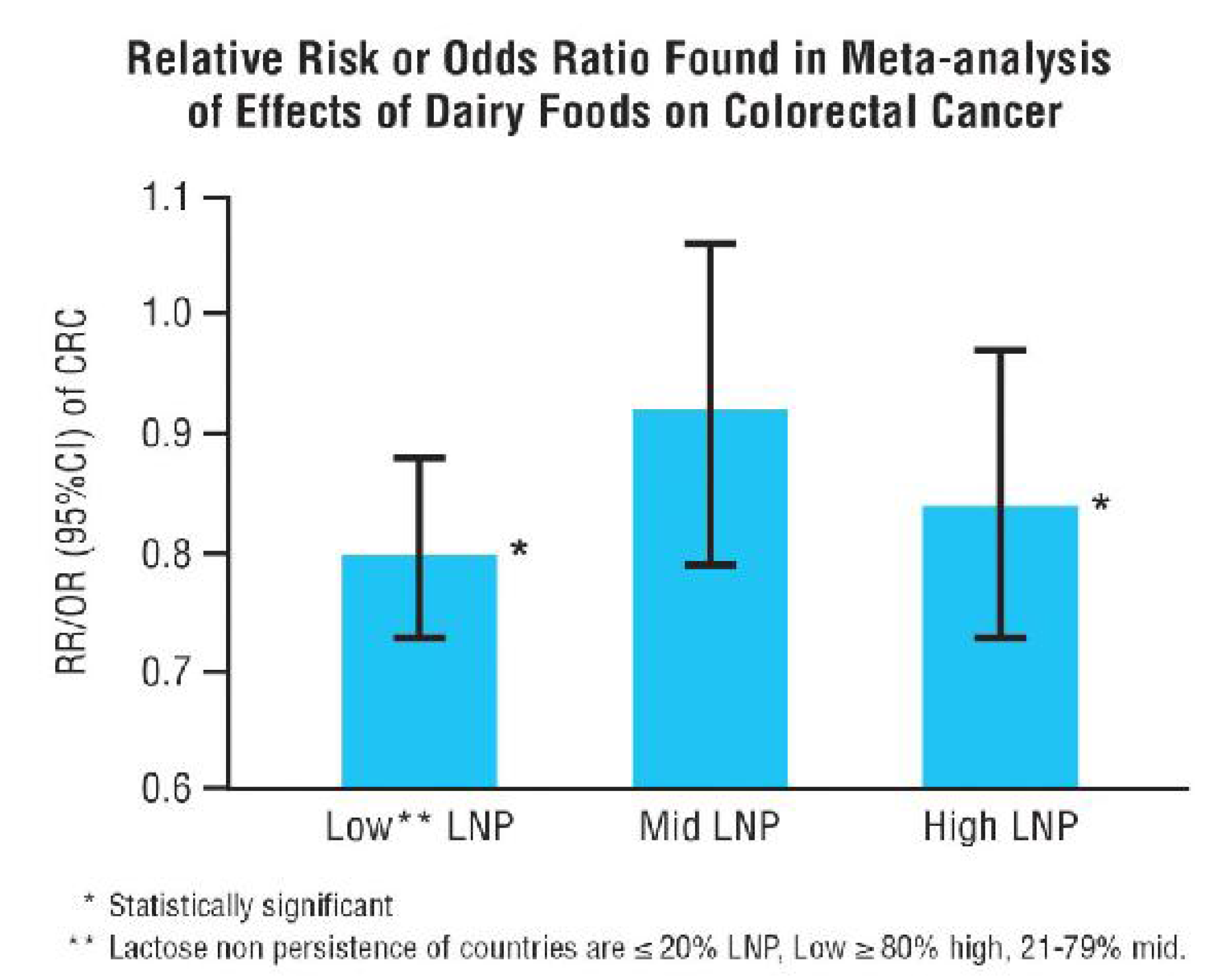



Nutrients Free Full Text Adaptation To Lactose In Lactase Non Persistent People Effects On Intolerance And The Relationship Between Dairy Food Consumption And Evalution Of Diseases Html




Ppt Limited Dependent Variables Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube
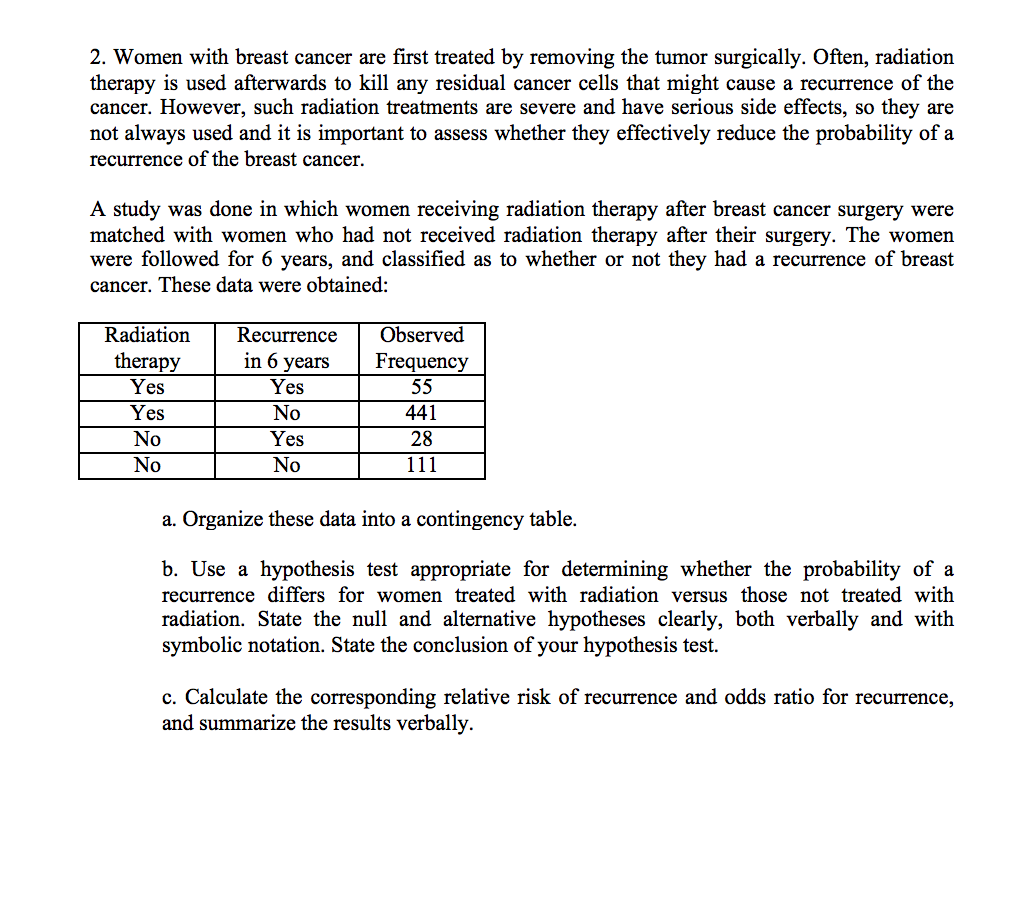



Solved I Can T Figure Out Number 2 I Don T Know Which Fo Chegg Com




Evidence Based Medicine Part 4 An Introduction To Critical Appraisal Of Articles On Harm
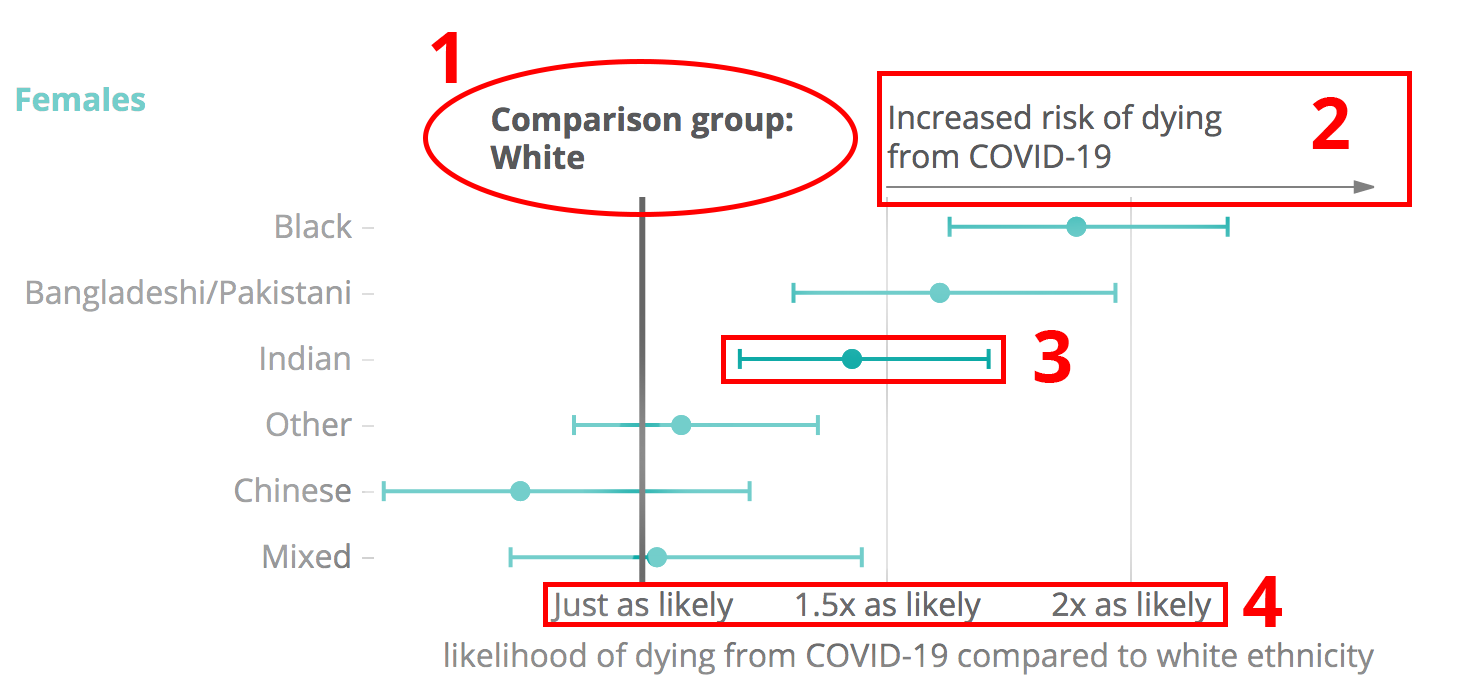



Against All Odds How To Visualise Odds Ratios To Non Expert Audiences Henry Lau




Measurements Of Risk Association Ppt Download



Arxiv Org Pdf 1510
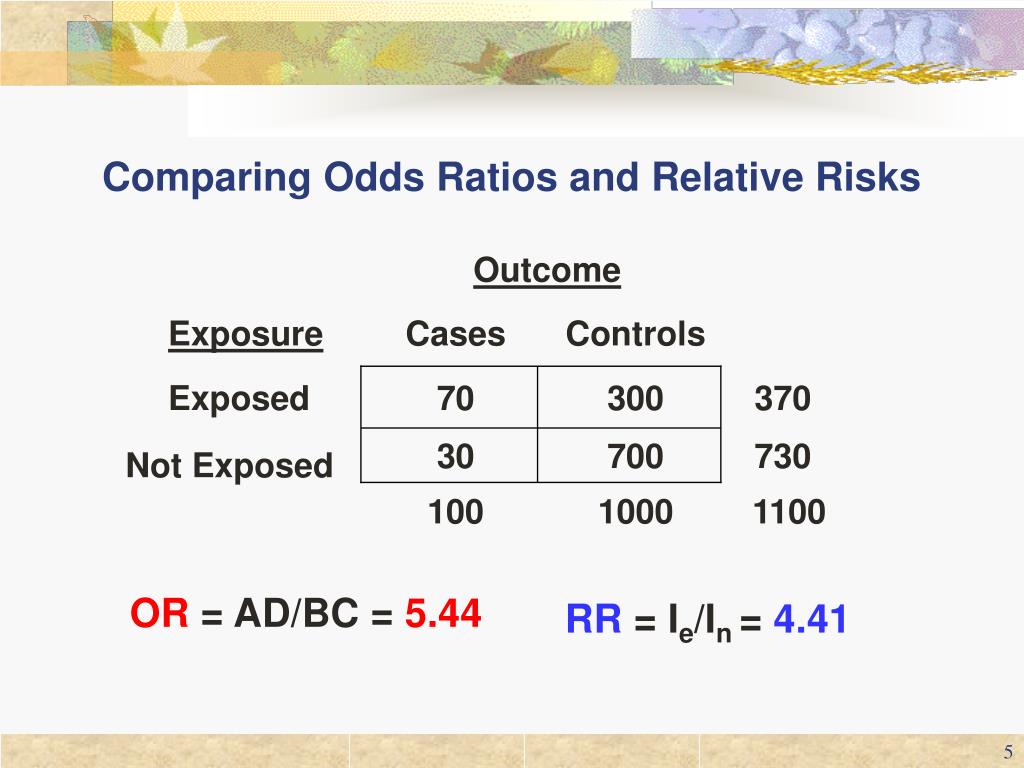



Ppt Case Control Study Design Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Odds Risks And Other Numbers Needed To Complicate Things Choi 16 Anaesthesia Wiley Online Library




Completeness Of Reporting And Risks Of Overstating Impact In Cluster Randomised Trials A Systematic Review The Lancet Global Health




A Most Odd Ratio American Journal Of Preventive Medicine




Logistic Regression Circulation



Risk A Statistician S Viewpoint Speaker Deck




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿